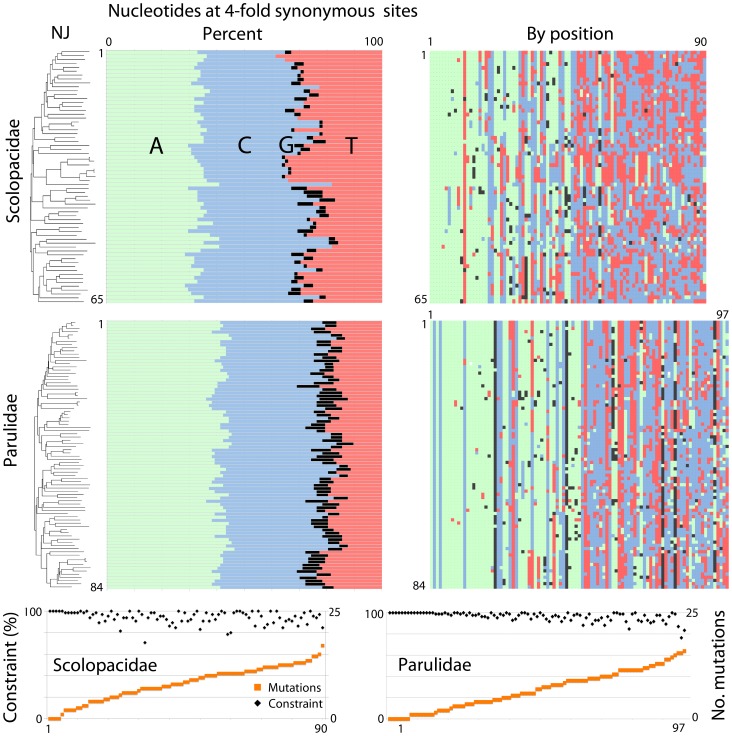
Figure 2. Constrained synonymous variation.
From left, COI NJ tree (n = 65 Scolopacidae, 84 Parulidae species), nucleotide composition at four-fold synonymous sites by species (A, adenine, green; C, cytosine, blue; G, guanine, black; T, thymine, red), and by position are shown (n = 90 Scolopacidae, 97 Parulidae sites in 519 nt COI segment). For the latter, positions are sorted by number of apparent mutation events according to NJ tree. At bottom, number of apparent mutation events and percent constraint (limited to one or two nucleotides) for each position are shown. Evidence for restricted variation includes unequal nucleotide composition; unequal distribution of mutation events according to predominant nucleotide (positions with predominantly A have fewer mutation events than those with T or C); and nucleotide composition largely constrained to one or two nucleotides at all sites regardless of number of mutation events.