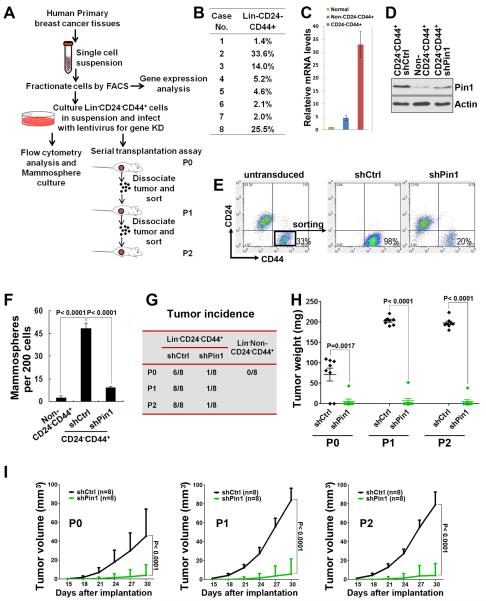
Figure 7. Pin1 regulates the expansion and tumorigenicity of human primary BCSCs.
A, schematic of the experiments on freshly isolated primary human BCSCs.
B, Lin−CD24−CD44+ cells were sorted from breast cancer tissues of eight patients, with percentage ranged from 1.4–33.6%.
C, real-time PCR showed that expression of Pin1 mRNA was markedly increased in the Lin−CD24−CD44+ population, comparing to the Lin−Non-CD24−CD44+ or normal epithelial cells.
D, western blot showed upregulated Pin1 expression in the BCSC-enriched population and the knockdown of Pin1 in the Lin−CD24−CD44+ population isolated from primary human breast cancer cells.
E, Pin1 KD decreased the CD24−CD44+ population. Lin−CD24−CD44+cells sorted from primary human breast cancers were infected with lentivirus expressing control or Pin1 shRNA, and then analyzed for the CD24−CD44+ population.
F, Pin1 KD decreased the mammosphere formation in Lin−CD24−CD44+ cells isolated from primary human breast cancer.
G–I, Pin1 KD interfered with both tumor initiation and growth of primary BCSCs in vivo, as shown by tumor incidence (G), tumor weights (H) and growth curve (I). 2,000 lentivirus transduced Lin−CD24−CD44+ cells freshly isolated from eight breast cancer patients were serially transplanted as xenografts into eight nude mice. P0, freshly isolated primary cells; P1, passage 1; P2, passage 2.
In all panels, error bars represent SD.