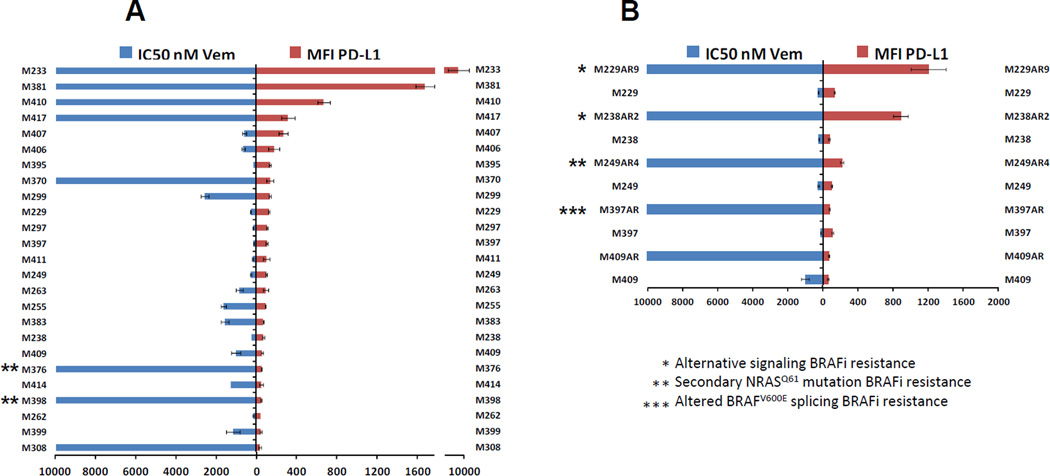
Figure 2. Comparison of PD-L1 expression in BRAF mutated melanoma cell lines with their responses to the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib.
A) Expressions of PD-L1 in BRAF mutated cell lines and their levels of sensitivities to the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib were graphed side by side. Each assay was performed twice and resistance to vemurafenib was defined as an IC50 of higher than 1000nM. B) Side by side expression of PD-L1 and the IC50 levels of five pairs of sensitive parental cell lines and their in vitro developed vemurafenib resistant sublines indicated by the AR suffixes after the cell lines names. Mechanism of resistance due to the activation of alternative pathways, secondary NRAS mutation and truncated BRAF has been indicated by one, two or 3 asterisks, respectively. In both graph A and B, a bimodal pattern of PD-L1 expression among the highly resistant cell lines can be seen.