Fig. 2.
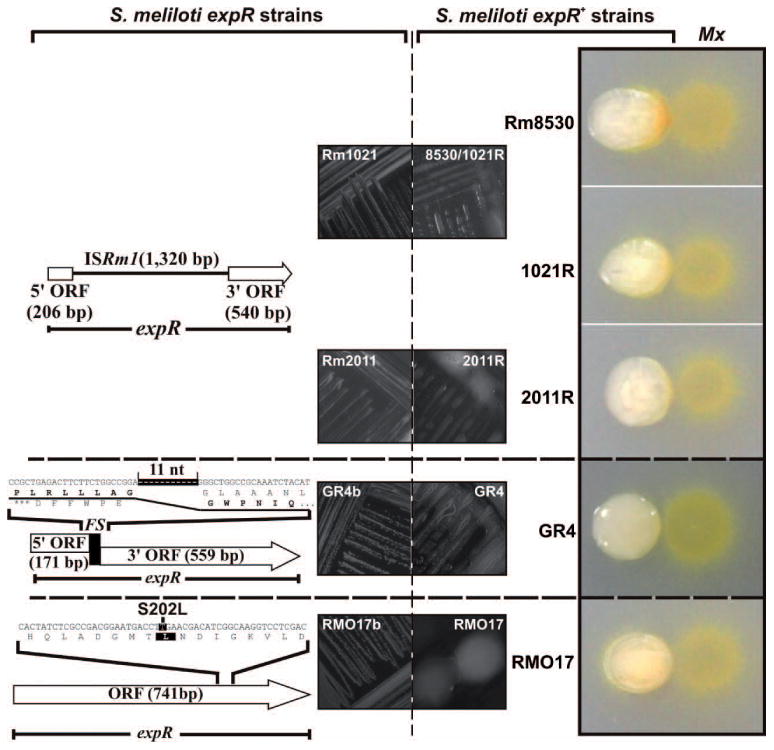
The wolfpack-like attack of M. xanthus DK1622 on S. meliloti requires a functional rhizobial expR gene. Diagrams of the spontaneous mutations of expR in the S. meliloti laboratory strains Rm1021 and Rm2011 (insertion of ISRm1), GR4b (frameshift deletion) and RMO17b (S202L), and their associated non-mucoid phenotypes on plates are shown in the left panels. M. xanthus preys on these strains by a frontal attack as shown in Fig. 1. The expR+ engineered derivatives (Rm8530, 1021R, 2011R) or natural variants (GR4 and RMO17) of these strains exhibit a mucoid phenotype and a wolfpack-like pattern in co-culture with M. xanthus (Mx) as shown in the images to the right.
