Fig. 4.
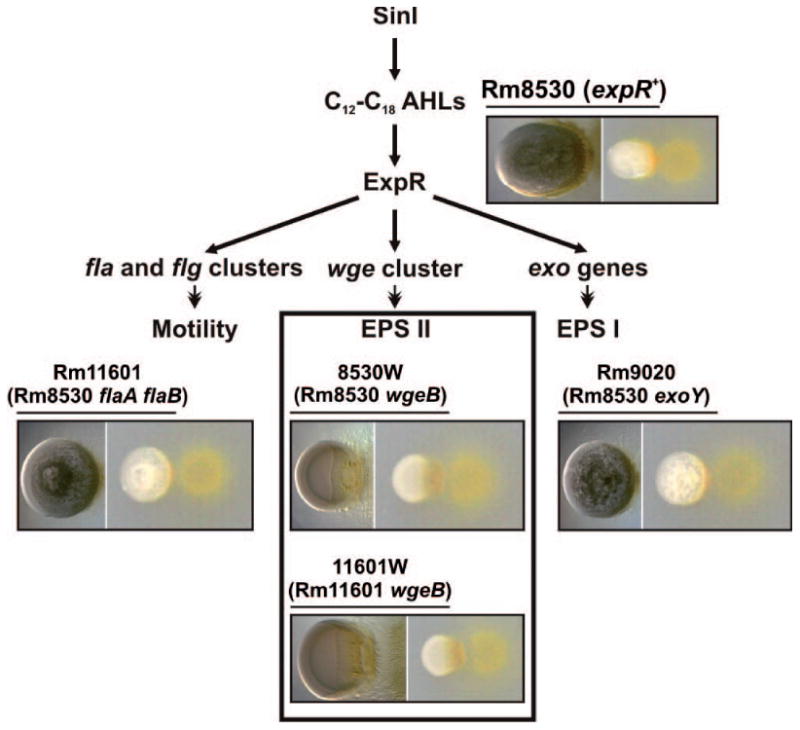
The rhizobial galactoglucan determines the predatory pattern of M. xanthus on S. meliloti. Simplified outline of the rhizobial functions influenced by the ExpR/Sin quorum sensing system. S. meliloti Rm8530 (expR+) and derivative strains harboring mutations impairing biosynthesis of EPS II/EPS I or motility (specified in brackets under the name of each strain) were subjected to predation tests on CTT agar. Images of the S. meliloti-M. xanthus cocultures taken 72 h after spotting are shown below the name of each rhizobial strain. Microscopic images of the S. meliloti colonies are shown to the left in each case. Only strains devoid of EPS II (inset) suffered a prolonged frontal attack.
