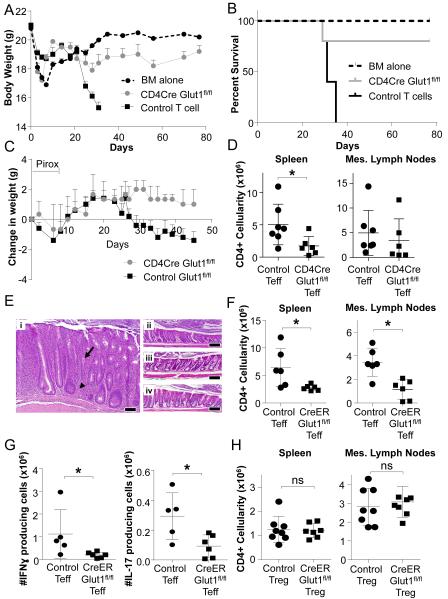
Figure 7. Glut1 is selectively required for Teff, but not Treg, expansion and function in inflammatory disease.
(A, B) GvHD was induced with transplant of T cell-depleted bone marrow (BM) or BM + control (Glut1fl/fl or Glut1fl/+) or CD4CreGlut1fl/fl T cells into allogeneic hosts and (A) body weight and (B) survival were measured over time. (C-D) Naïve control (Glut1fl/fl) or CD4CreGlut1fl/fl T cells were transferred into Rag1−/− hosts and colitis was triggered 2 weeks later via piroxicam (Pirox; day 0 on start of Pirox) exposure and (C) animal weights measured over time, or (D) mice were sacrificed at day 30 and the number of CD4 T cells present in the spleen and mesenteric (mes) lymph nodes determined by flow cytometry. (E-H) Rag1−/− mice were injected with control (CreERGlut1+/+, Glut1fl/fl) or CreERGlut1fl/fl naïve T cells. Colitis was triggered by piroxicam exposure 2 weeks after T cell transfer. Animals were then treated with tamoxifen to activate Cre. (E) H&E histology of proximal colon from mice that received (i) naïve control T cells, (ii) naïve CreERGlut1fl/fl T cells, (iii) naïve control T cells plus control Treg, or (iv) naïve control T cells plus CreERGlut1fl/fl Treg. Bar indicates 100μm; arrow indicates cryptic abscess and arrowhead indicates a granuloma. (F) The number of CD4 or (G) IFNγ or IL-17 producing T cells in the mesenteric (mes) lymph nodes was determined after 4 weeks by flow cytometry. (H) Rag1−/− mice were co-injected with wild type naïve T cells and either control (CreERGlut1+/+, Glut1fl/fl) or CreERGlut1fl/fl nTreg. Mice were treated after 2 weeks with piroxicam and tamoxifen to trigger IBD and activate Cre and CD4 T cells were determined after 4 weeks. Data are representative of 2 (A-B) or 3 (C-H) independent experiments and show mean clinical score ± SEM (A, C) or mean ± SD (D, F-H).