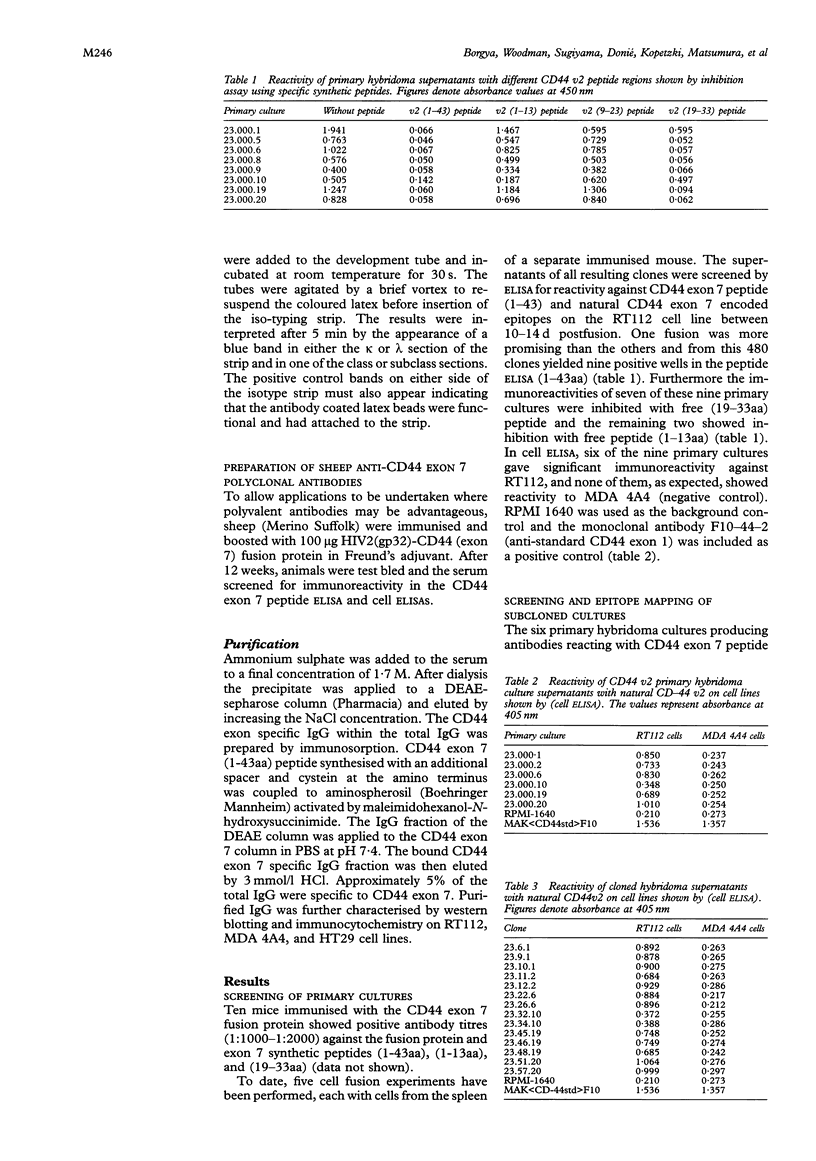
Abstract
Aims—Exon 7 of the human CD44 gene is overexpressed in many commonly occurring carcinomas. The aim of the study was to explore the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of this frequent abnormality.
Methods—A new monoclonal antibody (mAb, M-23.6.1) and a polyclonal antibody (pAb,S-6127) to the corresponding antigen were raised by immunising mice and sheep, respectively, with a specially constructed fusion protein HIV2 (gp32)-CD44 exon 7.
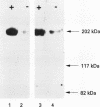
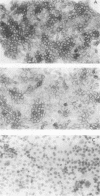
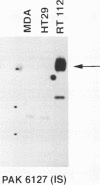
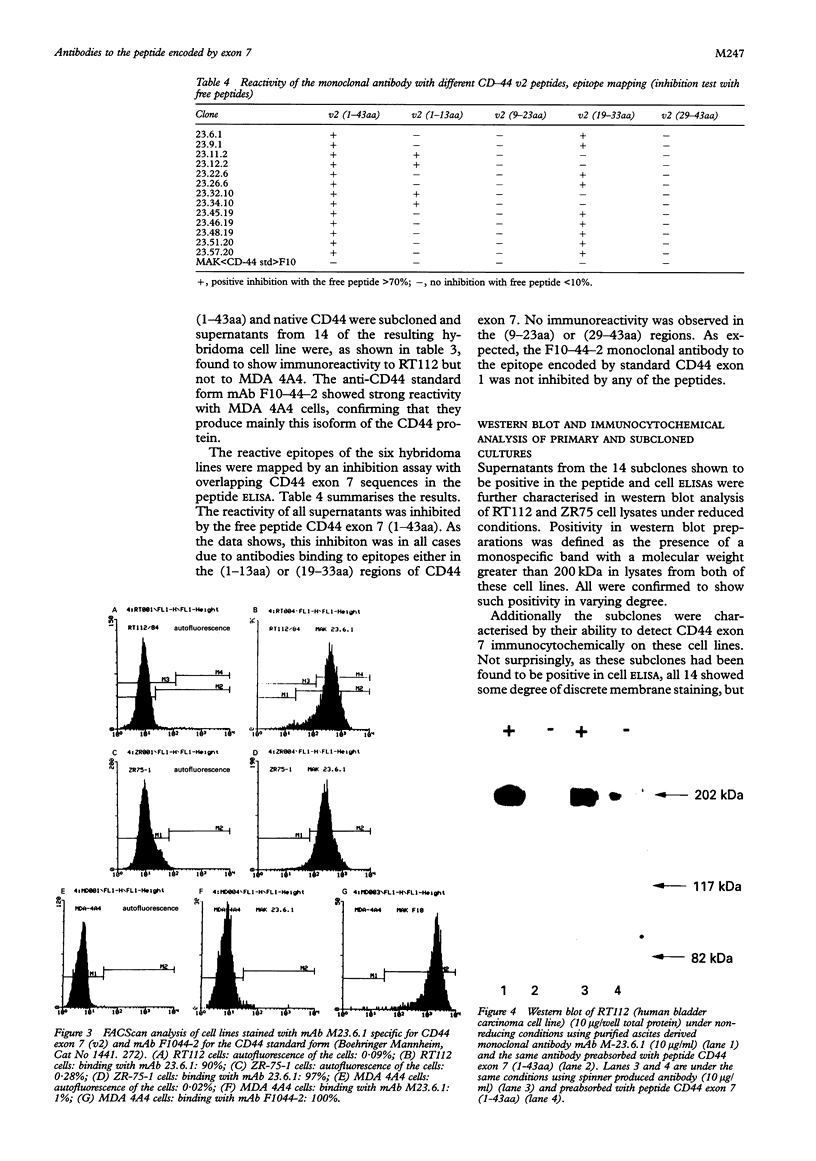
Results—Characterisation of mAb, M-23.6.1 by ELISA, western blotting, immunocytochemistry, and FACS analysis confirmed that it specifically recognises an epitope in the region between amino acids 19 and 33 of the peptide encoded by this exon. Western blotting experiments with two cell lines, RT112 and ZR75-1, known from RT-PCR data to be overtranscribing the exon, yielded a monospecific band of approximately 220 kDa, and immunocytochemistry showed discrete membrane staining on the same cell lines. Fluorescent antibody cell sorting (FACS) revealed binding to greater than 90% of the cells of each of these lines. Specificity of recognition of the antigen was shown by inhibition of the precise immunoreactivity typically seen in ELISA and Western blots, by pre-incubation with synthetic exon 7 peptide or fragments of it.
Conclusions—The new antibodies will be useful tools for the further analysis of abnormal CD44 isoforms and their clinical implications.
Keywords: CD44 antibodies
Keywords: tumour marker
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Stamenkovic I., Melnick M., Underhill C. B., Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1303–1313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90694-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Wayner E. A. Characterization of the class III collagen receptor, a phosphorylated, transmembrane glycoprotein expressed in nucleated human cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4193–4201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Wayner E. A., Hoffman P. A., St John T., Butcher E. C., Carter W. G. Structural homology between lymphocyte receptors for high endothelium and class III extracellular matrix receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4654–4658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heider K. H., Dämmrich J., Skroch-Angel P., Müller-Hermelink H. K., Vollmers H. P., Herrlich P., Ponta H. Differential expression of CD44 splice variants in intestinal- and diffuse-type human gastric carcinomas and normal gastric mucosa. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 15;53(18):4197–4203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochuli E., Döbeli H., Schacher A. New metal chelate adsorbent selective for proteins and peptides containing neighbouring histidine residues. J Chromatogr. 1987 Dec 18;411:177–184. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93969-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S., Bargatze R. F., de los Toyos J., Butcher E. C. Lymphocyte recognition of high endothelium: antibodies to distinct epitopes of an 85-95-kD glycoprotein antigen differentially inhibit lymphocyte binding to lymph node, mucosal, or synovial endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):983–990. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen S., Jalkanen M., Bargatze R., Tammi M., Butcher E. C. Biochemical properties of glycoproteins involved in lymphocyte recognition of high endothelial venules in man. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1615–1623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann M., Heider K. H., Sinn H. P., von Minckwitz G., Ponta H., Herrlich P. CD44 variant exon epitopes in primary breast cancer and length of survival. Lancet. 1995 Mar 11;345(8950):615–619. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90521-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Terpe H. J., Stauder R., Marston W. L., Stark H., Günthert U. Expression and modulation of CD44 variant isoforms in humans. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):71–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y., Hanbury D., Smith J., Tarin D. Non-invasive detection of malignancy by identification of unusual CD44 gene activity in exfoliated cancer cells. BMJ. 1994 Mar 5;308(6929):619–624. doi: 10.1136/bmj.308.6929.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y., Tarin D. Significance of CD44 gene products for cancer diagnosis and disease evaluation. Lancet. 1992 Oct 31;340(8827):1053–1058. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93077-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Screaton G. R., Bell M. V., Jackson D. G., Cornelis F. B., Gerth U., Bell J. I. Genomic structure of DNA encoding the lymphocyte homing receptor CD44 reveals at least 12 alternatively spliced exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12160–12164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Amiot M., Pesando J. M., Seed B. A lymphocyte molecule implicated in lymph node homing is a member of the cartilage link protein family. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1057–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90638-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama M., Woodman A., Sugino T., Crowley S., Ho K., Smith J., Matsumura Y., Tarin D. Non-invasive detection of bladder cancer by identification of abnormal CD44 proteins in exfoliated cancer cells in urine. Clin Mol Pathol. 1995 Jun;48(3):M142–M147. doi: 10.1136/mp.48.3.m142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe K. K., Ellis L. M., Saya H. Expression of CD44R1 adhesion molecule in colon carcinomas and metastases. Lancet. 1993 Mar 20;341(8847):725–726. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90490-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underhill C. B., Green S. J., Comoglio P. M., Tarone G. The hyaluronate receptor is identical to a glycoprotein of Mr 85,000 (gp85) as shown by a monoclonal antibody that interferes with binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13142–13146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wielenga V. J., Heider K. H., Offerhaus G. J., Adolf G. R., van den Berg F. M., Ponta H., Herrlich P., Pals S. T. Expression of CD44 variant proteins in human colorectal cancer is related to tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4754–4756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]