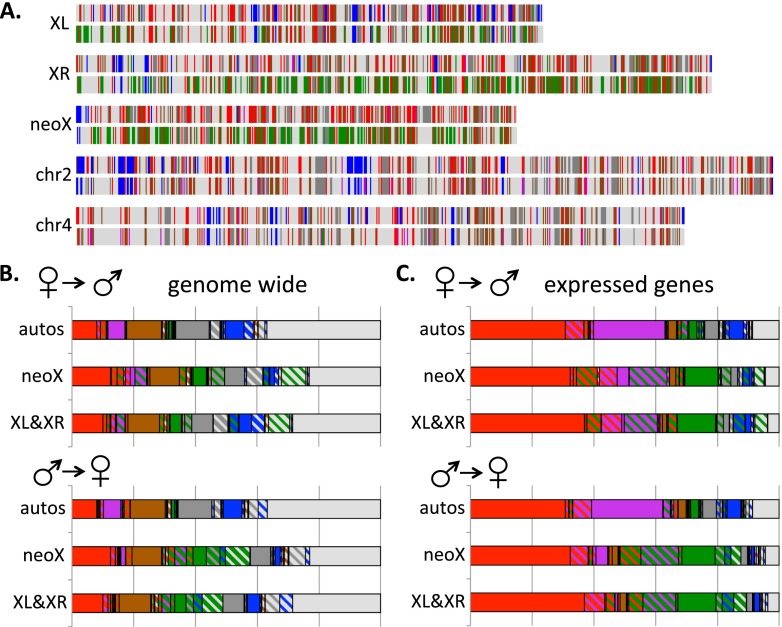
Figure 3.
The sex-specific chromatin landscape in D. miranda, and transitions in chromatin states between sexes. (A) A genome-wide karyotype view of the chromatin domains derived from female larvae (top) and male larvae (bottom) smoothed across 50-kb windows. (B) Transitions of chromatin states across chromosomes between the sexes. The solid background color indicates the fraction of a particular state in a given sex, and the crosshatch color indicates transitions to a given state in the other sex; solid regions indicate regions in the same chromatin state in both sexes. (C) Same as B, but for genomic regions overlapping the CDS of actively transcribed genes (FPKM > 1).