Figure 9.
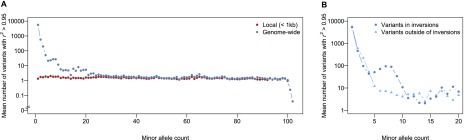
Relationship between LD and minor allele count. For each of the minor allele counts, 1000 random variants are sampled, and the mean number of variants genome-wide or locally (<1 kb) in strong LD (r2 > 0.95) with the focal variant is calculated. (A) Relationship between the mean number of variants in strong LD with the focal variant and minor allele count. (B) Relationship between the mean number of variants in strong LD with the focal variant and minor allele count, stratified according to the location of the focal variant (within or outside of inversions).
