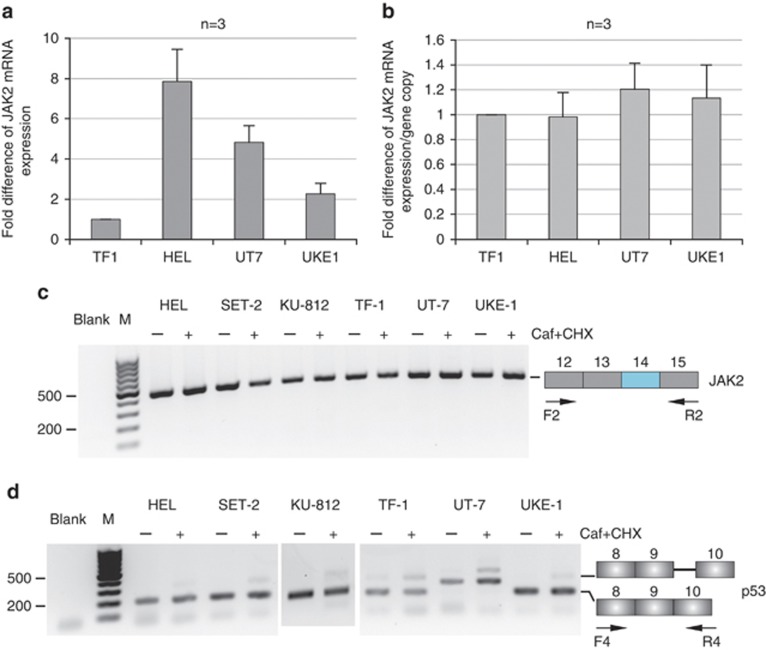
Figure 2.
mRNA analysis. (a, b) JAK2 steady-state mRNA expression. Real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR experiments were performed on cells expressing either the wild-type (WT) JAK2 or the JAK2V617F variant. Primers for the PCR step were designed upstream of the exon 14 mutation, within exon 8 (forward primer) and exon 9 (reverse primer) (Supplementary Table 2). Data were expressed as fold difference of JAK2 mRNA level relative to TF-1 single gene copy, and standardized to SDHA mRNA expression13 (a). JAK2 mRNA steady-state level per gene copy was determined for each cell line (b). (c, d) JAK2 mRNA splicing analysis. JAK2 mRNA deriving from the WT or JAK2V617F allele was analyzed by RT-PCR, using pairs of primers surrounding exon 14 (Supplementary Table 2). Cells were treated with caffeine (Caf) and cycloheximide (CHX) to stabilize nonsense mRNA molecules.11 RT-PCR experiments were performed on untreated (−) or treated (+) cells. No abnormal mRNA species was detected at exon 14 and flanking exons (c). An alternative splicing event, generating the inclusion in mature p53 mRNA of an additional sequence from intron 9, leads to the accumulation of a nonsense p53 mRNA species. This alternative splicing event was analyzed concomitantly in the same samples (d) to ascertain the efficiency of cell treatment. In this splicing event, 133 bp of p53 intron 9 are included in the mRNA. After treatment with caffeine and cycloheximide, two bands at 174 and 307 bp were visible on agarose gel, whereas only the 174 bp band was visible in the absence of cell treatment (d). In the UT-7 cell line, the same pattern is observed, although the two bands were higher than expected. Most likely, an additional splicing event must occur specifically in this cell line.