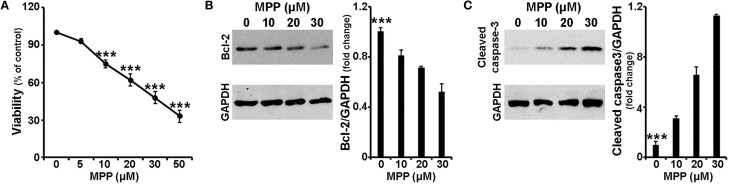
Figure 1.
MPP+ induced neurotoxicity in cortical neurons. Seven-day primary cortical neurons were treated with various concentrations of MPP+ for 24 h. (A) Cell viability following dose-dependent treatments was assayed by measuring MTT reduction by live neurons. Note that a significant reduction in neuronal viability was observed upon treatment with 10, 20, 30, and 50 μM, but not 5 μM, of MPP+. (B,C) Equal amounts of total protein from lysates of cortical neurons cultured for 24 h in the presence of 10, 20, and 30 μM MPP+ were analyzed on 12% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies specific for BCL-2 (B) and cleaved caspase-3 (C). To ensure equal loading, membranes were re-probed against GAPDH. Note that compared to untreated controls, primary cortical neurons treated for 24 h with MPP+ displayed a dose-dependent decrease of BCL-2 protein levels, as well as a dose-dependent increase of cleaved caspase-3 protein levels. Quantification of the results in (B,C) was performed by scanning densitometry. Bars in all the presented graphs depict mean ± s.e.m. ***P ≤ 0.001.