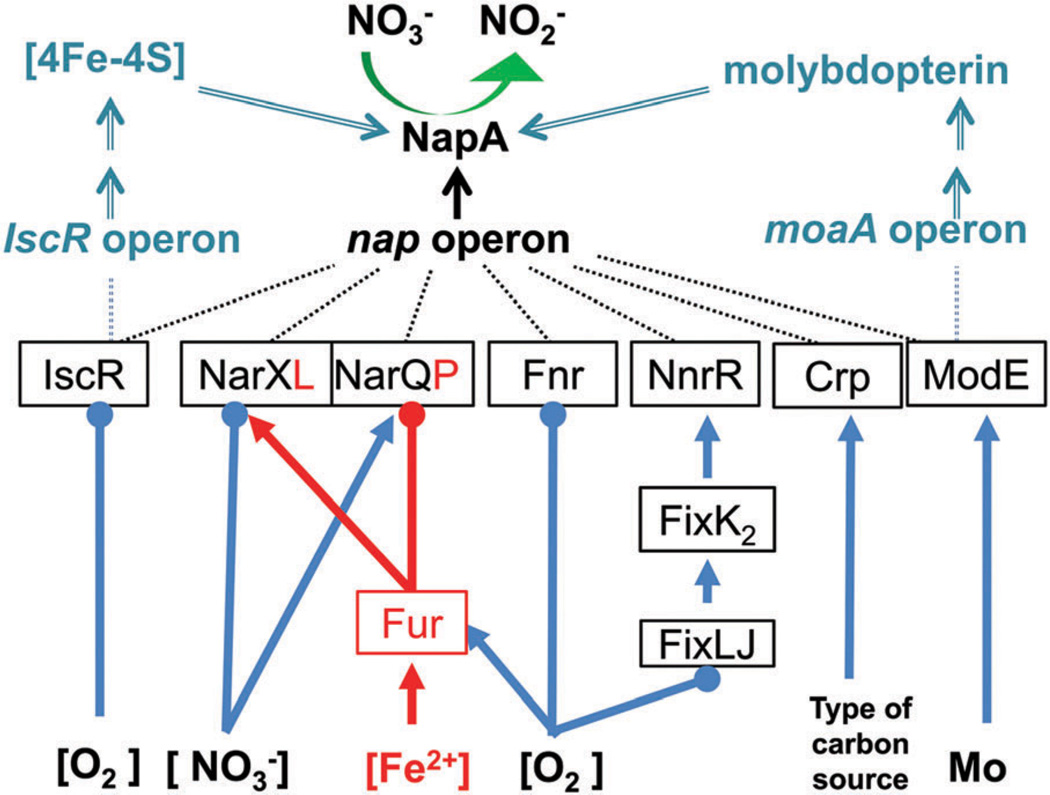
Fig. 17.
Transcriptional regulation of the nap operon, and the pyranopterin and [4Fe–4S] cofactor biogenesis operons. Note that not all regulatory effects are present in the same organism. Proteins directly regulating the nap operon transcription are connected to “NapA” with a dashed line (–), and those that affect the cofactor biogenesis operons are connected to the specific operons by a double dashed line (==). The operons for pyranopterin and [4Fe–4S] cofactor biogenesis (blue) are moaABCDE and iscRSUA-hscBA-fdx, respectively. Lines with arrow (→) denote a positive regulatory effect, i.e., up-regulation, in the presence of the associated environmental signal; negative effects, i.e., down-regulation, is indicated with circle lines (−•). Concentration dependent regulation is indicated with brackets surrounding the chemical, for example [O2].