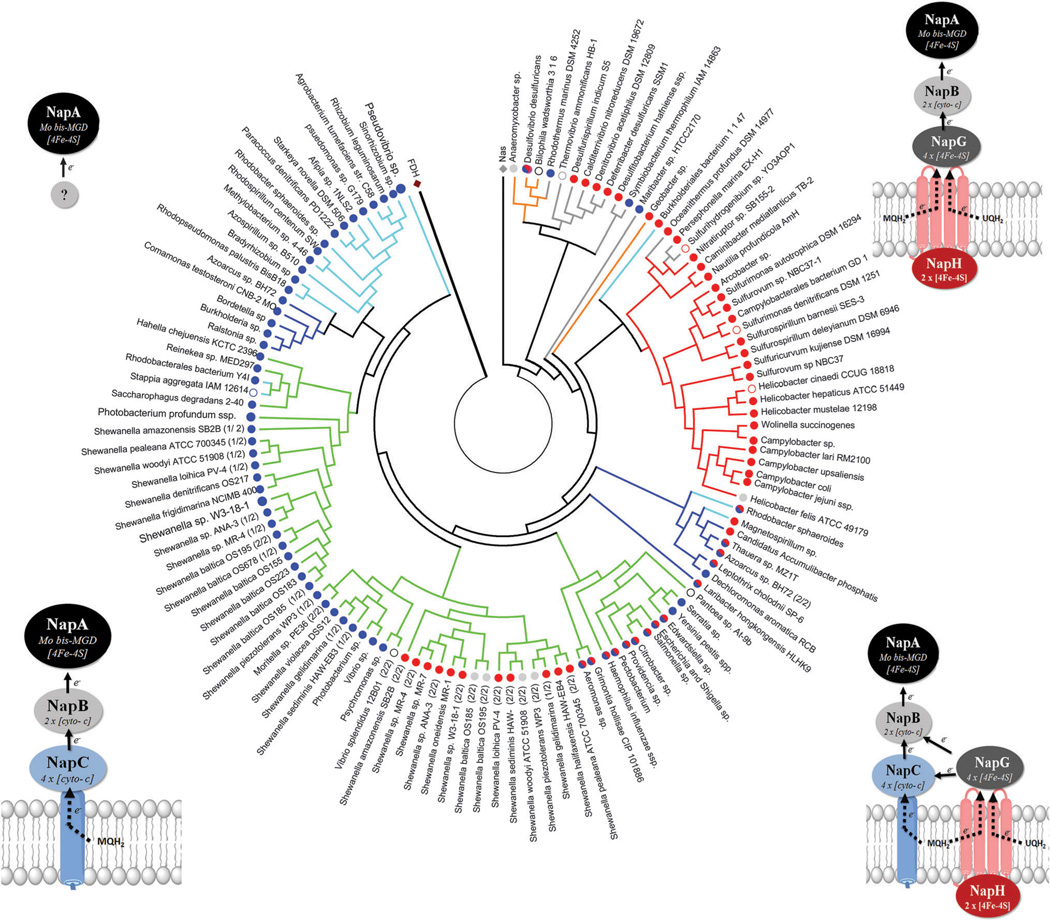
Fig. 18.
Phylogenic tree of NapA using 292 protein sequences. Positions containing gaps were eliminated, yielding a total of 600 amino acid positions in the final dataset. MEGA5 software was used for alignments and phylogenetic analyses. Formate dehydrogenase (FDH) was included in the analysis as an outlier. Three assimilatory nitrate reductases (Nas) were also included for reference. NapA sequences were collected from the NCBI database. Branches corresponding to similar species (sp.) or subspecies (ssp.) are collapsed. Branches are colored according to the phyla of proteobacteria: alpha (aqua); beta (navy blue); gamma (green); delta (orange); epsilon (red); non-proteobacteria (grey). Branch nodes are colored red (NapH); blue (NapC); red/blue (NapH + NapC); grey (no quinone oxidase). Diagrams at the four corners display the topology of the different Nap forms with respect to the periplasmic membrane and correspond to the node colors. Open circles represent NapA sequences from organisms where complete nap operon content is unknown.