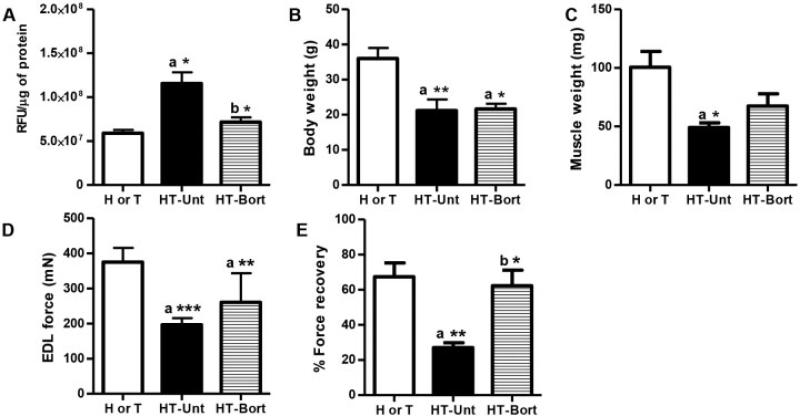
Figure 4.
Bortezomib (Bort) treatment improves muscle function in the mouse model of myositis. Major histocompatibility complex–overexpressing double-transgenic (HT) myositic mice and single-transgenic (H or T) control mice were divided into 3 groups: H or T (n = 5), untreated (Unt) HT (n = 4), and bortezomib-treated HT (n = 4). Bortezomib (0.75 mg/kg body weight) was injected intraperitoneally twice a week for 4 weeks. A, Proteasomal activity in quadriceps muscle lysates, shown as relative fluorescence units (RFU) normalized to protein units. B, Body weight. C, Gastrocnemius muscle weight. D, Maximal muscle force, determined by in vitro testing of extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles. E, Percent force recovery for extensor digitorum longus muscle. Values are the mean ± SEM. * = P < 0.05; ** = P < 0.01; *** = P < 0.001 versus H or T control mice (a) or versus untreated HT mice (b), by one-way analysis of variance.