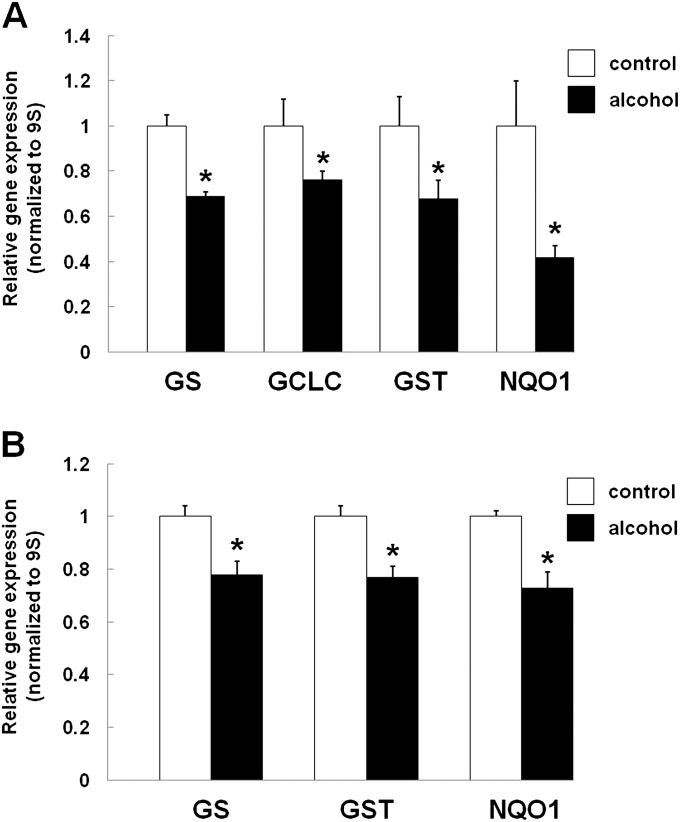
Figure 2.
Alcohol inhibits the expression of antioxidant response element (ARE)–regulated antioxidants. (A) Sprague-Dawley rats were fed an isocaloric liquid diet ± alcohol for a minimum of 10 weeks. Type II AECs were isolated and grown in culture for 7 days and the relative gene expression of glutathione (GSH) synthetase (GS), glutamate-cysteine ligase, catalytic subunit (GCLC), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dehydrogenase-quinone-1 (NQO1) quantified by PCR, as described in the Materials and Methods. GS, GCLC, GST, and NQO1 expression were significantly decreased (*P < 0.05) in the AECs from alcohol-fed rats. (B) L2 cells (rat AEC line) were exposed to alcohol (0.2%) for 72 hours and the relative gene expression of GS, GST, and NQO1 quantified by PCR, as described in the Materials and Methods. The expression of GS, GST, and NQO1 were significantly decreased (*P < 0.05) to 77, 77, and 73% of control levels, respectively.