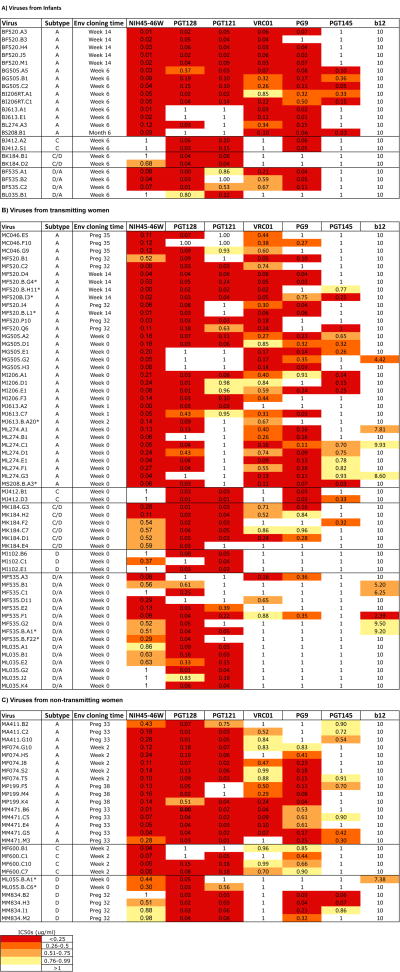
Figure 1. Summary of neutralization sensitivity profiles of all mother –infant viruses against bNAbs.
Viruses have been grouped into three panels representing (A) viruses obtained from infants, (B) viruses obtained from transmitting mothers and (C) viruses obtained from non-transmitting mothers. Each row represents (from left to right) the virus name, virus subtype based on V1-V5 envelope sequence, the time of sample from which envelope was isolated and the IC50 values for all bNAbs tested. Viruses were obtained as described previously [26, 33]. Maternal PBMC variants were obtained from blood samples collected at various weeks of pregnancy (preg) and after delivery (week) and the time ranged from preg 32 to week 14 (Week 0 refers to the first week post-partum). Breast milk variants were obtained from week 0, 2 and 14 and are indicated with an asterisk. All infants were HIV-DNA negative at birth. Infant samples were obtained from the first time-point at which infants tested HIV-DNA positive (week 6 or 14 and month 6). IC50 values range from 0.001-1μg/ml except for b12 (2.39-10μg/ml) and are grouped by quartiles as shown in the key to the upper right. Darker shading indicates increasing bNAb potency defined in the key at the bottom left. White color indicates that 50% neutralization was not achieved at the highest concentration of bNAb tested 1μg/ml or 10μg/ml for the case of b12. IC50s are an average of at least two independent experiments performed in duplicates.