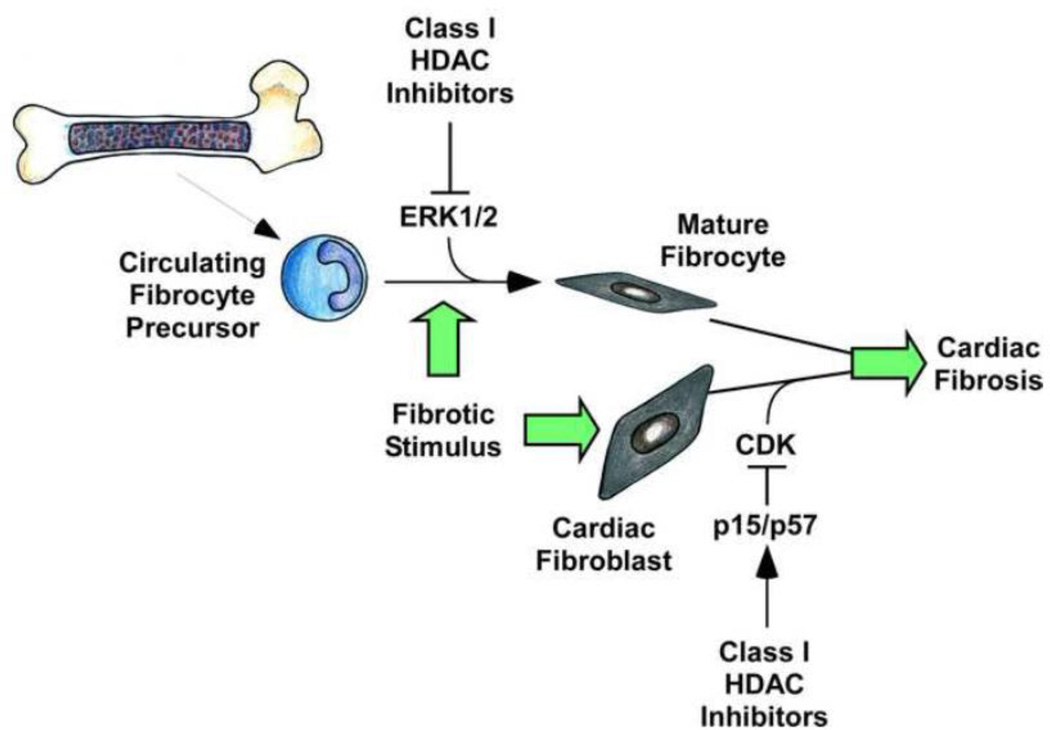
Figure 3. Mechanisms by which class I HDAC inhibition blocks cardiac fibrosis.
Class I HDAC inhibition prevents the differentiation of bone-marrow derived fibrocytes into active fibrocytes and fibroblasts through inhibition of ERK1/2 activation. Class I HDAC inhibition arrests cardiac fibroblasts in G0/G1 of the cell cycle via upregulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors p15 and p57. Both of these processes result in decreased numbers of activated ECM-producing fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in the myocardium, leading to decreased fibrosis.