Figure 5. Endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in coronary arteries from control, IUGR, melatonin and IUGR + melatonin animals.
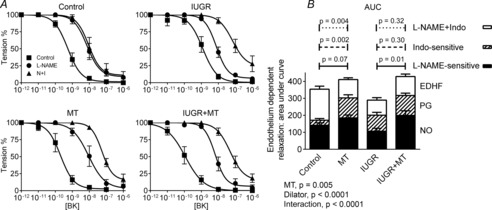
A, The endothelium was stimulated using bradykinin (BK) in arteries submaximally preconstricted with U46619. Nitric oxide (NO) and prostanoid (PG) production were blocked using l-NAME (N) and indomethacin (I, Indo), respectively. pD2 values for these curves shown in Table 3. B, Vasorelaxation attributable to NO, PG and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF) for each animal were derived and analysed using ANOVA. There were highly significant effects of treatment (IUGR and/or melatonin, MT) and dilator, with a significant interaction, indicating different contributions of dilator/treatment in the different treatment groups. Tukey's post hoc test P values for l-NAME and Indo-sensitive responses and the responses remaining in the presence of l–NAME + Indo, n = 6 per group.
