Figure 4.
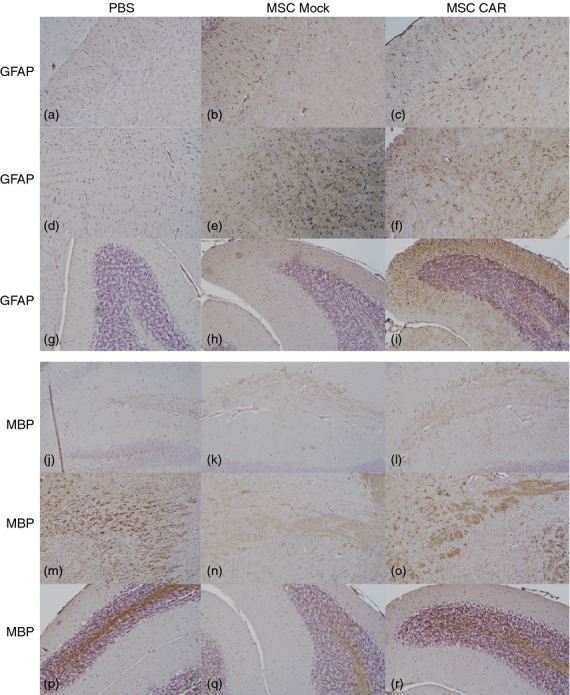
Effects of intranasally delivered CNS-targeted mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) on axonal damage and tissue recovery in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mice. Immunohistochemical staining for glial acidic fibrillary protein (GFAP) in corpus callosum (a–c), brainstem (d–f) and cerebellum (g–i) in brain sections from PBS-, MSC Mock- and MSC CARαMOG-treated EAE mice (15 days after i.n. treatment). In MSC CARαMOG-treated EAE mice there is strong staining in all areas (c,f,i). In MSC Mock-treated mice there is strong staining in all areas (b,e,h). In PBS-treated EAE mice there is weak staining (a,d,g). Immunohistochemical staining for myelin basic protein (MBP) in hippocampus (j–l), brainstem (m–o) and cerebellum (p–r) in brain sections from PBS-treated, MSC Mock-treated and MSC CARαMOG-treated EAE mice. In MSC CARαMOG-treated EAE mice there is strong staining of all areas (l,o,r). In MSC Mock-treated mice there is weak staining in all areas (k,n,q). In PBS-treated EAE mice there is moderate staining in hippocampus (j) and strong staining in brainstem and cerebellum (m,p). Original magnification 10×.
