Figure 4.
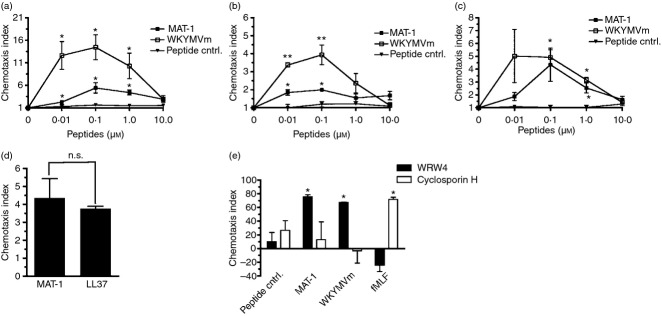
The peptide MAT-1 induces chemotaxis in primary neutrophils and monocytes. Chemotaxis was assessed using increasing concentrations of peptides in primary neutrophils (a) and monocytes were obtained by either positive selection (b) or negative selection (c). WKYMVm was used as a positive control for chemotaxis in both conditions. A negative peptide control was also used to compare with activity of MAT-1 and WKYMVm. The chemotaxis index is defined as fold change in average cells/field from media alone. Chemotaxis indices were compared at each concentration with a corresponding concentration of peptide control. Error bars represent SEM (n = 3, *P < 0·05, **P < 0·01). (d) The chemotactic activity of MAT-1 was compared with the known formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2) agonist LL-37 using primary neutrophils. Both MAT-1 and LL-37 were used at 100 nm concentrations (n.s. denotes no significant difference). (e) Chemotaxis inhibitors WRW4 and cyclosporin H were incubated for 15 min with neutrophils before determining chemotaxis in response to peptides. Chemotactic peptides were diluted to 100 nm for the control peptide, MAT-1, and WKYMVm, and 500 nm for fMLF. Per cent inhibition was calculated as reduction in chemotaxis index compared with pre-incubation with a vehicle control. Error bars represent SEM (n = 3, *P < 0·05).
