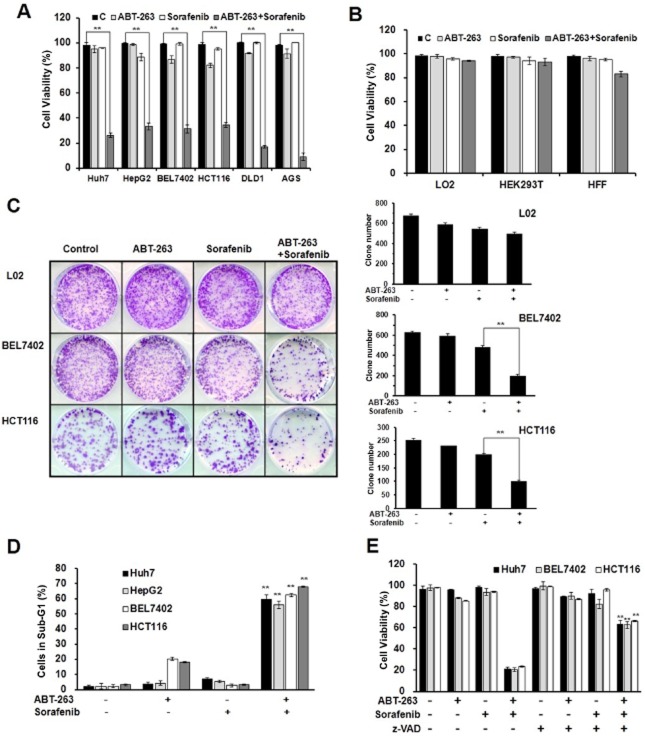
Figure 1.
The combination treatment of ABT-263 and sorafenib induces caspase-dependent apoptosis. The data represent the average of at least three independent experiments ± SD. **P < 0.01. (A) Huh7, HepG2, BEL7402, DLD1 and AGS cell lines were treated with 0.4 μM ABT-263 and 6 μM sorafenib either alone or in combination for 48 h, and the HCT116 cells were treated for 24 h, which were then assessed for cell viability using a trypan blue exclusion assay. (B) HEK293T, HFF and L02 cells were treated with 0.4 μM ABT-263 and 6 μM sorafenib either alone or in combination for 48 h. Cell viability was determined. (C) The cells were seeded in six-well plates and treated with ABT-263 and sorafenib, the HCT116 cells were treated for 24 h, and the BEL7402 and L02 cells were treated for 48 h. The attached cells were stained with crystal violet 10 days later. (D) FACS analysis of apoptosis following the treatment of ABT-263 (0.4 μM) and sorafenib (6 μM) either alone or in combination on the BEL7402, Huh7 and HepG2 cells for 48 h and the HCT116 cells for 24 h. The cells were dyed with 3 μL 10 mg·mL−1 PI and 10 μL 1 mg·mL−1 RNase, and the percentage of cells in sub-G1 determined. (E) The Huh7, BEL7402 and HCT116 cells were pretreated either with or without 50 μM z-VAD-fmk for 6 h, and then the trypan blue exclusion assay was performed to evaluate the cell viability after treatment with ABT-263 (0.4 μM) and sorafenib (6 μM) either alone or in combination. The percentage of cells dyed without trypan blue was determined.