Figure 2.
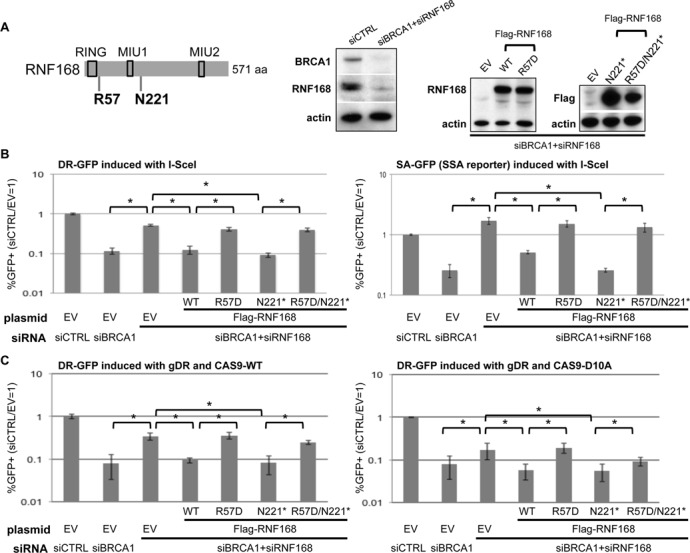
An N-terminal fragment of RNF168 (N221*) is proficient at inhibiting HR in BRCA1 deficient cells, in a manner dependent on the charge of R57. (A) Depletion of RNF168 and BRCA1 via siRNA and expression of RNF168 mutant forms. Shown is a diagram of RNF168 with approximate positions of the R57D and N221* mutations, as well as the RING, MIU1 and MIU2 motifs. Immunoblot signals are shown for BRCA1, RNF168 and actin for U2OS cells treated with siRNAs targeting BRCA1 and RNF168 (siBRCA1#6, siRNF168#18), and a non-targeting siRNA (siCTRL). Subsequent to siRNA treatment, cells were transfected with expression vectors for Flag-tagged RNF168 (WT, R57D, N221*, R57D/N221*, each resistant to siRNF168#18) or EV. Shown are immunoblot signals from these transfections for RNF168 (WT and R57D), Flag (N221* and R57D/N221*) and actin. (B) Analysis of RNF168 mutant forms for inhibition of I-SceI-induced HR in BRCA1 depleted cells. Two U2OS reporter cell lines that measure distinct types of HR were evaluated: DR-GFP that measures HDR and SA-GFP that measures SSA. These U2OS cell lines were treated with the siRNAs described in A and subsequently co-transfected with the expression vector for I-SceI along with the RNF168 expression vectors described in A, or the control EV. Shown are the frequencies of GFP+ cells for each reporter cell line, relative to parallel transfections with a non-targeting siRNA (siCTRL) and control EV. *P < 0.0001 (n = 6). (C) RNF168 influences HDR of CAS9-induced chromosomal breaks similarly to those induced by I-SceI. U2OS DR-GFP reporter cell line was transfected as in B, except replacing I-SceI with gRNA/CAS9 plasmids expressing gDR and CAS9-WT or CAS9-D10A, as shown in Figure 1. Frequencies of GFP+ cells were measured as in B. *P ≤ 0.022 (n = 6).
