Figure 6.
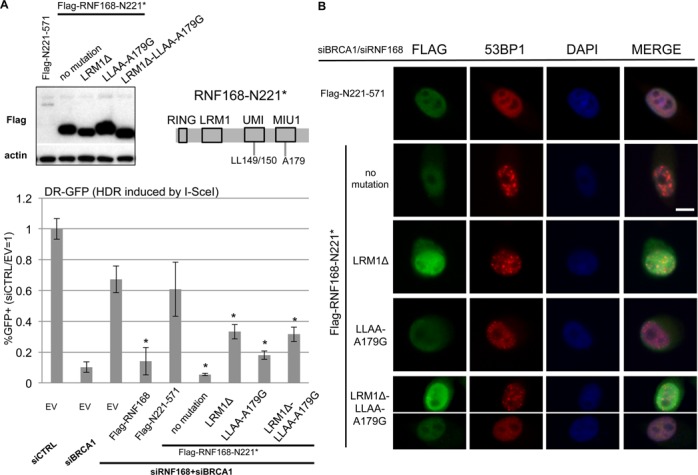
The LRM1 and ubiquitin binding motifs within RNF168-N221* are important but not essential for inhibition of HR. (A) Conserved motifs within N221* are important for inhibition of HDR. Shown is a diagram of N221* with the approximate positions of the LRM1 and UMI/MIU1 motifs. Also shown are immunoblotting signals for Flag and actin for cells transfected with a set of expression plasmids for Flag-RNF168-N221* with mutations in these conserved motifs, as well as Flag-RNF168-N221-571. U2OS DR-GFP cells were treated with siRNAs targeting BRCA1 and RNF168, and subsequently co-transfected with expression vectors for I-SceI and a set of RNF168 mutants. Shown are the frequencies of GFP+ cells for each reporter cell line, relative to parallel transfections with a non-targeting siRNA (siCTRL) and control EV. *distinct from EV, P < 0.0001 (n = 6). (B) RNF168 mutants that show at least intermediate inhibition of HR are also proficient for promoting 53BP1 IRIF. U2OS cells were treated with siCTRL or siBRCA1 and siRNF168 and subsequently transfected with Flag-tagged RNF168 expression vectors described in A. Subsequently, cells were treated with 6 Gy of IR (Cs137), and allowed to recover for 4 h prior to fixation and immunostaining. Shown are Flag and 53BP1 immunostaining, and DAPI staining images for representative cells from each transfection. The exposure times for each type of immunostain are the same for each cell. The cells were selected to represent the 53BP1 IRIF results for each RNF168 mutant as quantified in Table 2, but do not necessarily represent the average intensity of Flag staining for each RNF168 mutant, which can show variability among cells. Scale bar = 10 μm.
