Figure 1.
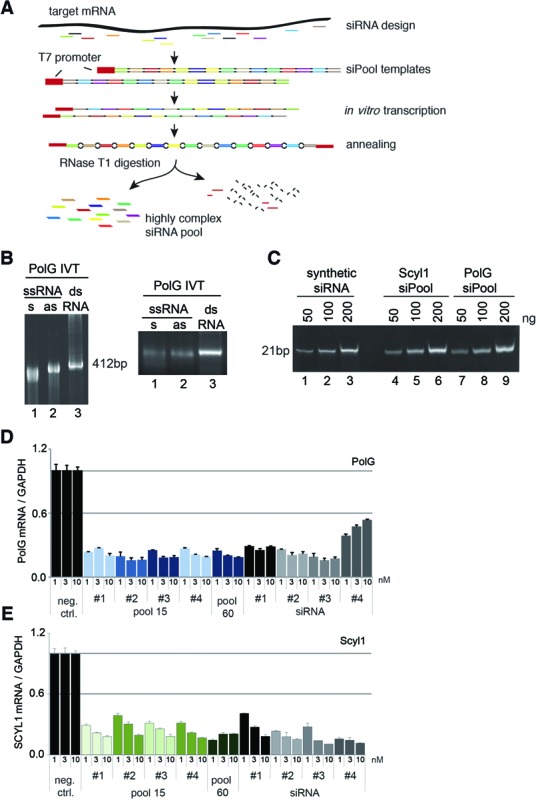
siPool generation and on-target activity. (A) Schematic overview of siPool construction. SiRNA sequences are designed and arranged in tandem separated by specific spacer sequences. siPool transcripts are in vitro transcribed by T7 polymerase and annealed. The resulting siPool precursors contain complementary siRNA sequences flanked by single-stranded spacer regions. The spacer sequences allow RNase T1 digestion resulting in double-stranded siRNAs with 2 nt 3′ overhangs. (B) In vitro transcription and annealing of siPools. 600 ng (left) or 800 ng (right) in vitro transcribed (IVT) sense and antisense strands (lanes 1 and 2) were annealed to a double-stranded siPool precursor (lane 3), loaded onto a 5% native polyacrylamide gel (left) or on a 1% native agarose gel (right). (C) Comparison of purified siPools with a synthetic siRNA. 50, 100 or 200 ng of purified siPools (lanes 4–9) or a synthetic siRNA (lanes 1–3) was loaded onto a 20% native polyacrylamide gel and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. (D and E) HeLa cells were transfected with 1, 3 or 10 nM concentrations of siPools containing 15 siRNAs (pool 15 #1–4), a combination of all 15 siRNA-siPools resulting in a siPool containing 60 different siRNAs (pool 60) or specific siRNAs (#1–4) directed against PolG (D) or Scyl1 (E).
