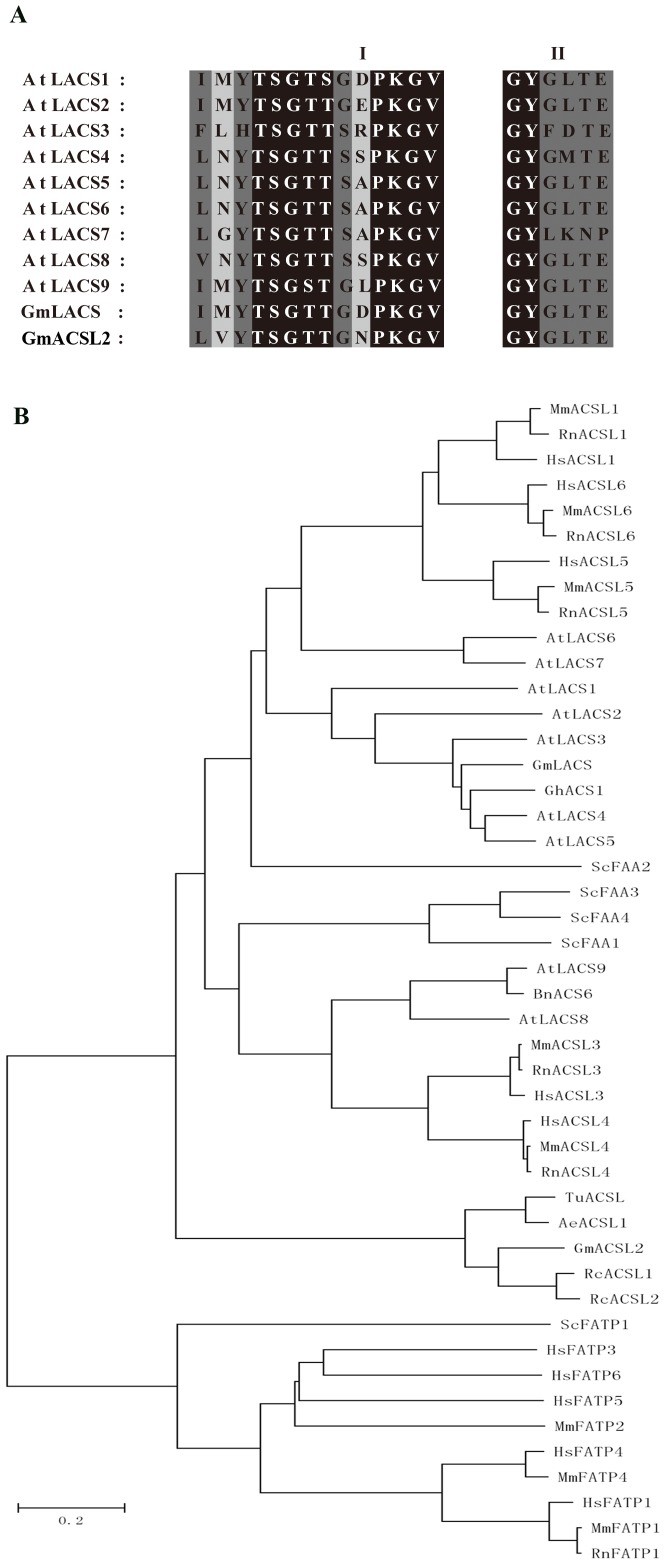
Figure 1. Sequence analysis of GmACSL2.
(A) Multiple amino acid sequences alignment of Glycine max GmACSL2 and GmLACS sequence with Arabidopsis thaliana AtLACS1 to AtLACS9. The I and II blocks of shadows indicate the highly conserved acid residues in AMP-binding protein. Black frames indicate the higher conservation amino acids, dark grey frames indicate the conservation amino acids, and light frames indicate the lower conservation amino acids. The protein follows: AtLACS1 (AAM28868), AtLACS2 (AAM288689), AtLACS3 (AAM28870), AtLACS4 (AAM28871), AtLACS5 (AAM28872), AtLACS6 (AAM28873), AtLACS7 (AAM28874), AtLACS8 (AAM28875), and AtLACS9 (AAM28876). (B) Phylogenic analysis between GmACSL2 with other ACSL enzymes and FATP proteins from plant, mammalian and yeast. The ACSL enzymes include G.max GmLACS, Arabidopsis thaliana AtLACS1-9, Gossypium hirsutum GhACS1 (ABA00144), Brassica napus BnACS6 (CAC19877), Ricinus communis RcACSL1 (XP_002520618) and RcACSL2 (XP_002520615), Aegilops tauschii AeACSL1 (EMT11835), Triticum urartu TuACSL (EMS60031), Homo sapiens HsACSL1 (NP_001986), HsACSL3 (NP_004448), HsACSL4 (NP_004449), HsACSL5 (NP_057318), and HsACSL6 (NP_056071), Mus musculus MmACSL1 (NP_032007), MmACSL3 (XP_129894), MmACSL4 (NP_062350), MmACSL5 (AAH31544), and MmACSL6 (NP_659072), Rattus norvegicus RnACSL1 (NP_036952), RnACSL3 (NP_476448), RnACSL4 (NP_446075), RnACSL5 (NP_446059), and RnACSL6 (NP_570095), and Saccharomyces cerevisiae ScFAA1 (P30624), ScFAA2 (P39518), ScFAA3 (P39002), and ScFAA4 (P47912). FATP proteins include Homo sapiens HsFATP1 (NP_940982), HsFATP3 (NP_077306), HsFATP4 (Q6P1M0), HsFATP5 (Q9Y2P5), and HsFATP6 (NP_001017372), Mus musculus MmFATP1 (NP_036107), MmFATP2 (AAC40186), and MmFATP4 (XP_130079), Rattus norvegicus RnFATP1 (NP_036119), and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (EWH19453). The bars stand for evolutionary distance. Bar = 0.2.