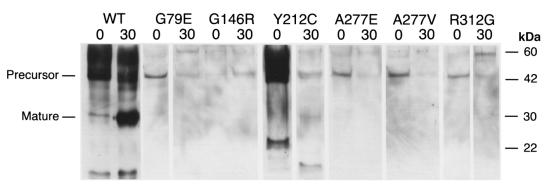
Figure 2.
Immunoblot of mutant and wild-type cathepsin K proteins. Aliquots of Pichia pastoris culture supernatants, before and after 30 min of pepsin treatment (indicated as 0 and 30, respectively), were electrophoresed in SDS-PAGE and transferred to blots that were hybridized with polyclonal rabbit anti–human cathepsin K antibodies. The wild-type cathepsin K (WT) proenzyme (lane 1) was detected at a higher than expected molecular mass, which resolved after pepsin digestion (lane 2). Molecular mass standards (measured in kDa) are indicated in the right margin. There was no immunologically detectable cathepsin K protein in supernatants from pPIC9K vector–only control (data not shown). The G146R precursor protein, which was less abundant before pepsin treatment in this Western blot, was more abundant at 0 min than at 30 min in all subsequent repetitions