Figure 3.
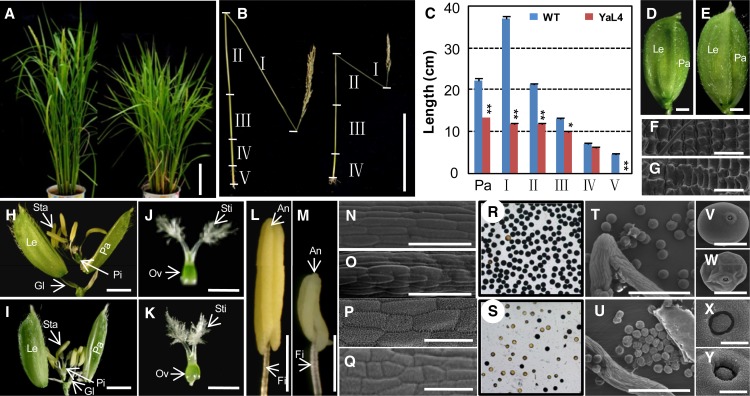
Phenotypic comparisons of wild-type and OsY14a-RNAi transgenic rice plants. A, Rice plants at the heading stage of the wild type (left) and OsY14a-RNAi line 4 (right). Bar = 20 cm. B, Internodes (I–V) and panicle of wild-type and YaL4 seeds after maturation. Bar = 20 cm. C, Size quantification of the internodes (I–V) and panicle (Pa) between the wild type (WT) and YaL4. Significance was evaluated by two-tailed Student’s t test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. D and E, Florets of the wild type and YaL4. Bars = 1 mm. F and G, Epidermal cells on lemma of the wild type and YaL4 by scanning electron microscopy. Bars = 50 µm. H and I, Artificially opened florets of the wild type and YaL4. Bars = 1 mm. J and K, Pistils of the wild type and YaL4. Bars = 1 mm. L and M, Stamens of the wild type and YaL4. Bars = 1 mm. Glume (Gl), lemma (Le), palea (Pa), stamen (Sta), anther (An), filament (Fi), pistil (Pi), stigma (Sti), and ovary (Ov) are indicated in D, E, and H to M. N and O, Cells on filaments of the wild type and YaL4 by scanning electron microscopy. Bars = 50 µm. P and Q, Cells on anthers of the wild type and YaL4 by scanning electron microscopy. Bars = 50 µm. R and S, I2-KI-stained pollen grains of the wild type and YaL4. T to W, Pollen of the wild type and YaL4 by scanning electron microscopy at different magnifications. Bars = 200 µm (T and U) and 20 µm (V and W). X and Y, Germ pore of the wild type and YaL4 by scanning electron microscopy. Bars = 20 µm.