Figure 3.
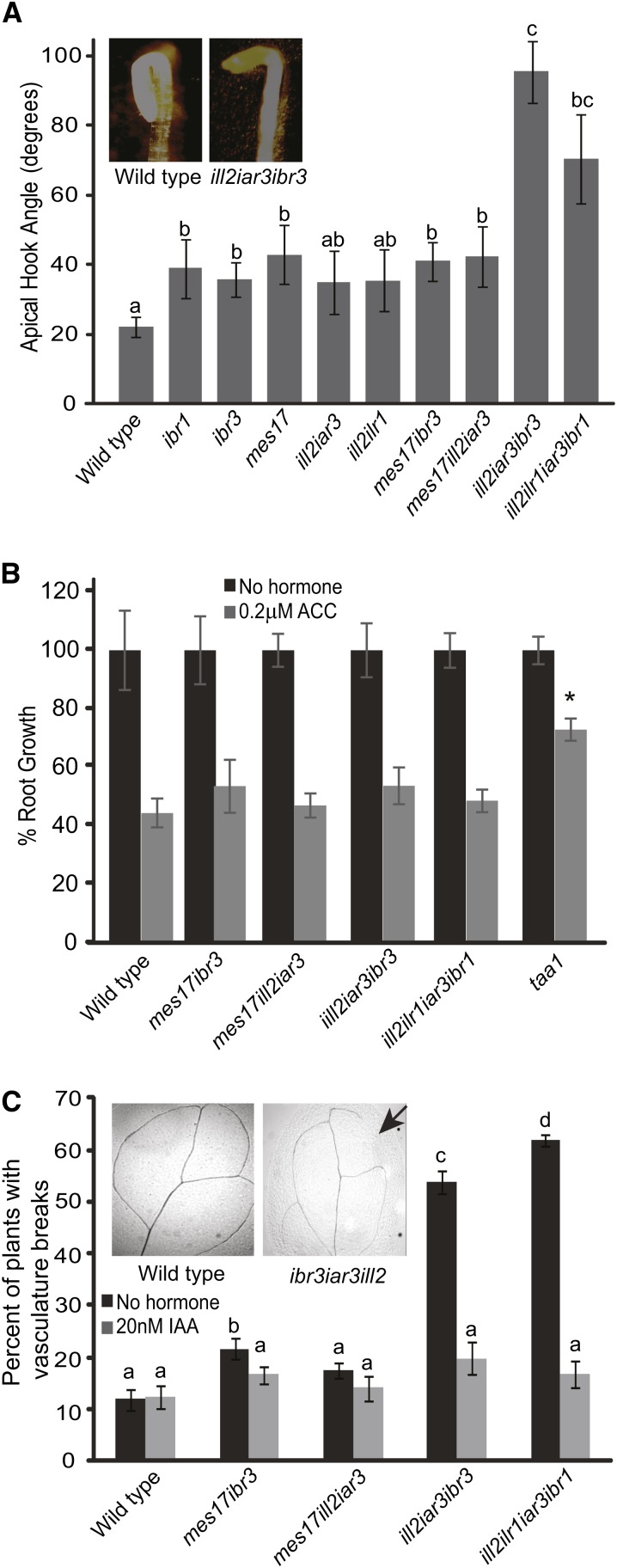
Combination mutants have phenotypes indicative of low auxin levels. A, Combination mutants have defects in apical hook maintenance compared with the wild type. Apical hooks were measured on seedlings grown 1 d in the light and 4 d in the dark. ImageJ software was used to measure the apical hook angle. Inset, One representative wild-type plant and one representative iar3 ill2 ibr3 plant. n ≥ 15; error bars represent se, and a to c indicate significant differences using one-way ANOVA (P < 0.05). B, Combination mutants show wild-type sensitivity to ethylene. Roots were measured from 5-d-old seedlings grown on no hormone or 0.2 µm ACC. Data are shown as percent root growth compared with no hormone controls. A taa1 single mutant is included as an ACC-resistant control. n ≥ 10; error bars represent se. *, Statistically significant result by Student’s t test compared with the wild type under the same conditions (P < 0.05). C, Combination mutants have breaks in vasculature tissue that could be rescued by IAA application; 7-d-old cotyledons were cleared and imaged after growth on media with no hormone or supplemented with 20 nm IAA. The graph shows the percentage of plants with cotyledon breaks. Inset, One representative wild-type leaf and one ill2 iar3 ibr3 leaf. The arrow indicates a break in vein pattern. n ≥ 35; a to d indicate significant differences using one-way ANOVA (P < 0.05).