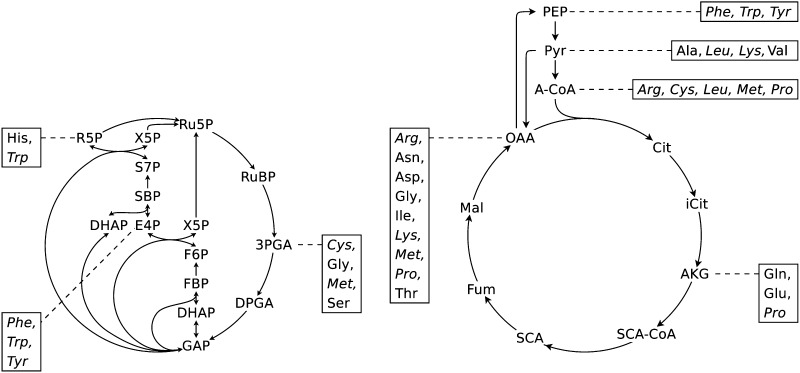
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the most basic biochemical pathways comprising the metabolic precursors for the carbon skeletons of all amino acids. The list of pathways comprising the direct precursors is provided in Supplemental Data S1, Table S11. Amino acids highlighted in italics have more than one precursor. RuBP, Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate; 3PGA, 3-phosphoglycerate; DPGA, 1,3-diphosphoglycerate; GAP, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; FBP, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; F6P, fructose-6-phosphate; E4P, erythose-4-phosphate; X5P, xylulose-5-phosphate; SBP, seduheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate; S7P, sedoheptulose-7-phosphate; R5P, ribose-5-phosphate; Ru5P, ribulose-5-phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; Pyr, pyruvate; A-CoA, acetyl-CoA; Cit, citrate; iCit, isocitrate; AKG, α-ketoglutarate; SCA-CoA, succinyl-CoA; SCA, succinate; Fum, fumarate; Mal, malate; OAA, oxalacetate.