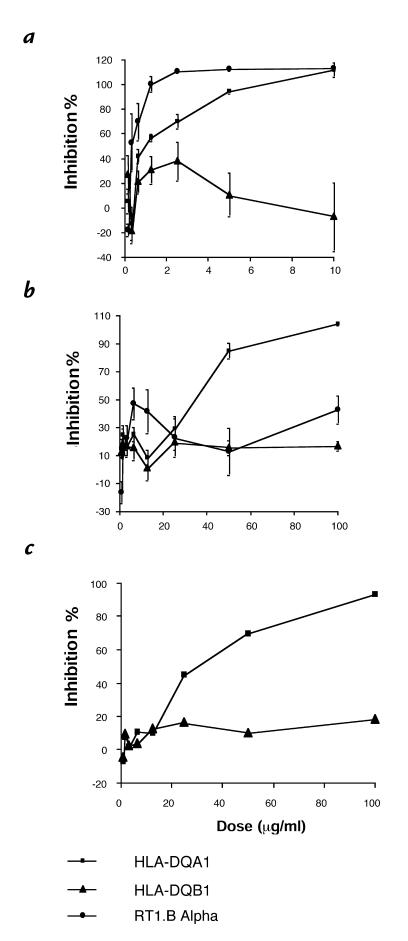
Figure 1.
(a) Effects of peptides derived from HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, and RT1.Bα on the LEW–WFx rat MLR (n = 3). Peptide derived from RT1.Duα required a concentration of 250 μg/ml to cause 100% inhibition of proliferation (data not shown). (b) Effects of peptides derived from HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1 on the human MLR (n = 6). Results are expressed as percent inhibition of the proliferative response in the presence of the individual peptides and represent the mean ± SEM for each experiments. (c) Effects of peptides derived from HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1 on the mouse MLR. Results are expressed as percent inhibition of the proliferative response of the mouse MLR (C57/BL–DBAx) in the presence of the individual peptides and represent the mean of quadruplicate wells of a typical experiment. MLR, mixed lymphocyte response.