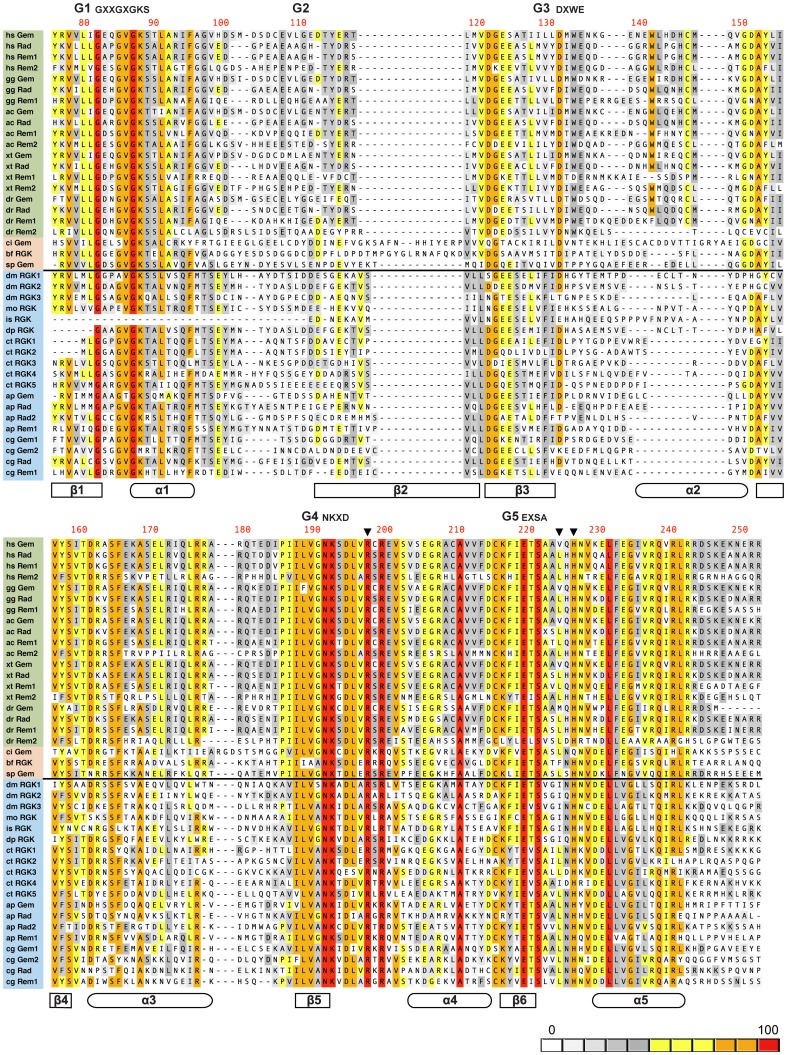
Figure 4. Alignment of RGK protein G-domains.
G-domain sequences were aligned using the ClustalW algorithm in MacVector (version 12.7.5). Sequence labels (left) are color coded with vertebrates in green, non-vertebrate deuterostomes in pink, and protostomes in blue. The black horizontal line divides the deuterostomes/protostome sequences. Organism genus and species abbreviations (e.g., hs for Homo sapiens) are depicted in Figure 3. The method for parsing the RGK protein G-domain sequence is documented in the text and supplement (table S1) along with GenBank accession numbers for each sequence. The G-motifs (G1–5) along with canonical RGK protein sequences for G1, G3, G4, and G5 are depicted above the alignments. The residue numbers are for human Gem (top row) and are right justified. The inverted black triangles represent key residues participating in RGK protein–Cavβ interaction[43]. Secondary structural domains (α-helices and β-sheets) are depicted schematically below the sequences. Sequence identity color scale is depicted in the lower right corner.