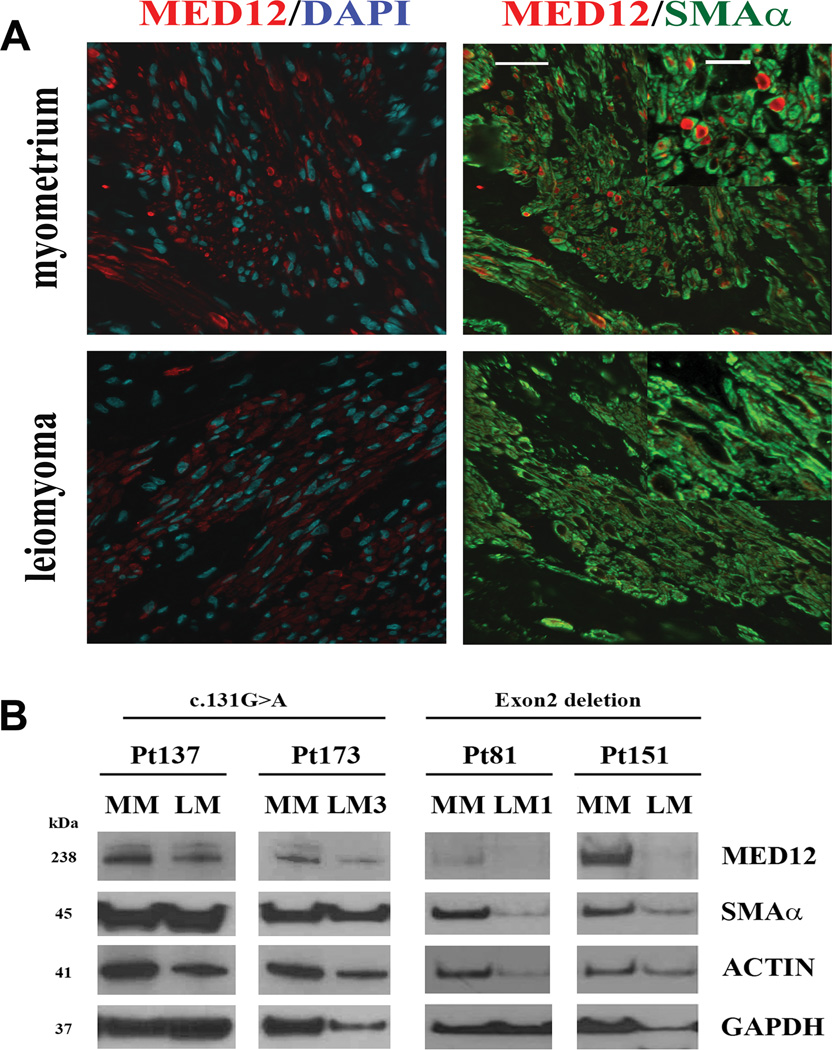
Figure 3.
Reduced MED12 protein levels in uterine leiomyomas with complex MED12 mutations. A. Confocal microscopic images illustrate an example of immunofluorescent staining for MED12 (red), smooth muscle actin (green) and DAPI (blue) in leiomyoma with a complex MED12 mutation (with a partial MED12 Exon 2 deletion) and its matched myometrium. In myometrium, the expression pattern and distribution are punctuated with high intensity staining enriched in perinuclear localization. In contrast, the expression pattern for leiomyoma is diffused in the cytoplasm and has lesser staining intensity. Scale bars = 50 µm. Higher power image of MED12 staining in leiomyoma and myometrium are shown in the insert (Scale bar = 25 µm). B. The expression of MED12 protein was detected by Western blot analysis in leiomyomas with complex MED12 mutations (Pt81LM and Pt151LM for Exon 2 deletion on right) and leiomyomas with simple MED12 point mutations (Pt137LM and Pt173LM for c.131G>A on left). MED12 expression in the matched myometrium (MM) was shown next to tumors. Anti-α-smooth muscle actin, Anti-Actin, and anti-GAPDH were used as protein loading controls.