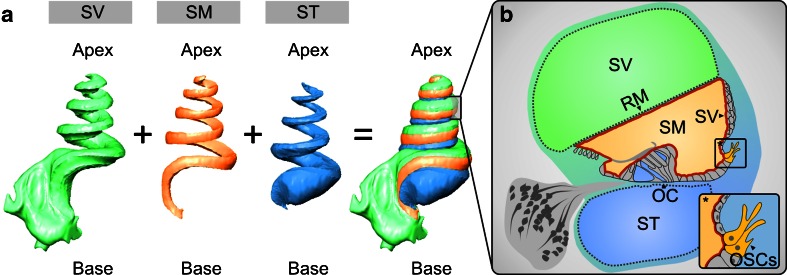
Fig. 1.
Three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of orthogonal-plane fluorescence optical sectioning (OPFOS) data from the guinea pig cochlea to demonstrate the anatomical relations of the cochlear fluid spaces. a 3D reconstruction of the endolymphatic space in the scala media (SM) and the perilymphatic spaces in the scala tympani (ST) and scala vestibuli (SV). b Schematic cross-sectional view of the guinea pig cochlear duct in the half-turn V. The cochlear duct epithelium and interepithelial tight junctions constitute the cochlear “perilymph–endolymph barrier” (PEB, red line) that encloses the endolymph in the SM. Two partitions of the cochlear PEB, namely Reissner's membrane (RM) and the organ of Corti (OC), directly separate the endolymph in the SM from the perilymph in the SV and ST. The stria vascularis (SV) does not form a direct epithelial barrier between the cochlear fluid compartments of SV, SM and ST. In the inlay *, the position of the outer sulcus cells (OSCs) in the cochlear duct epithelium is illustrated.