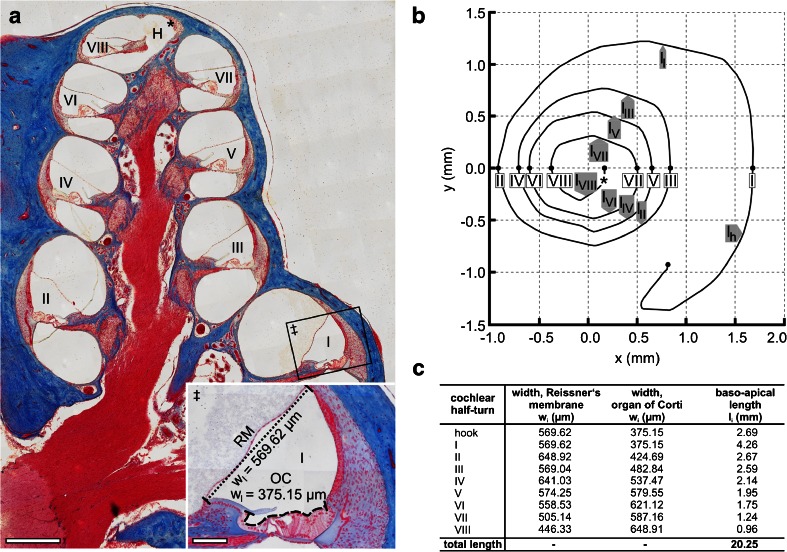
Fig. 4.
Determination of surface areas of the cochlear perilymph–endolymph barrier (PEB) on the adult guinea pig cochlea. a Overview of an azan-stained lateral (midmodiolar) section of the adult guinea pig cochlea. The width (radial length) of Reissner's membrane (RM) separating the SV from the SM (‡, dotted line) and the width of the apical surface of the organ of Corti (OC) separating the ST from the SM (‡, dashed line) were measured in all eight cochlear half-turns (WI–WVIII) (H, helicotrema; asterisk, apical end of the cochlear duct). b The baso-apical (longitudinal) length of RM and that of the OC were determined for each cochlear half-turn based on orthogonal plane fluorescence optical sectioning (OPFOS) data of the adult guinea pig cochlea, derived from Hofman et al. [32]. An OPFOS-based projection of the cochlear spiral in the XY plane (b, adapted from Hofman et al. [32] with permission from the corresponding author and the publisher, Wiley-Blackwell) was used to measure the longitudinal length of the eight cochlear half-turns (l I–l VIII) and the hook region (l h). c Results of width and length measurements determined in a and b. Scale bars: (a) 500 μm; (a, ‡) 100 μm