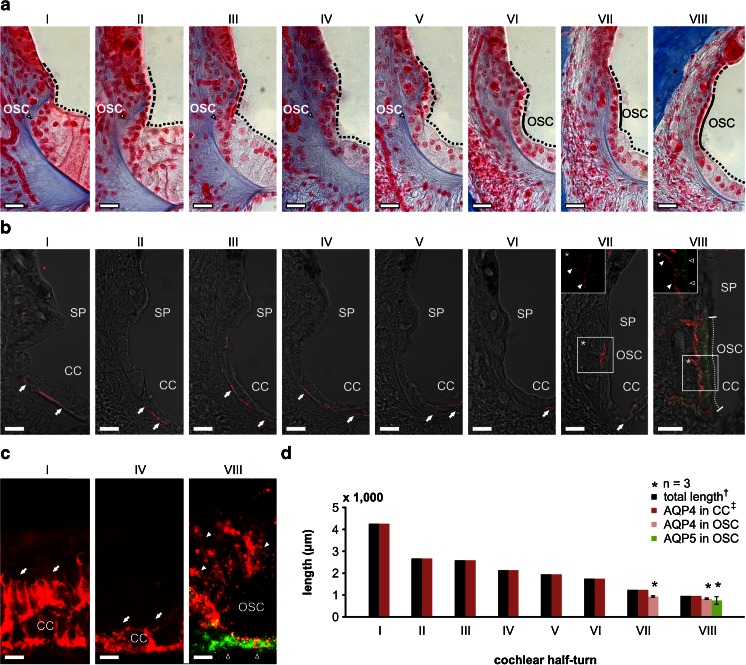
Fig. 5.
Complementary localisation of AQP4 and AQP5 in the apical and basolateral membranes of outer sulcus cells (OSCs) in the adult guinea pig cochlea. a The outer sulcus region in all eight cochlear half-turns (I–VIII) from azan-stained sections of the adult guinea pig cochlea. In cochlear half-turns I–V, the epithelial lining of the endolymphatic space in the outer sulcus region is formed by Claudius cells (CCs, black dotted lines mark the apical surface of CCs) and epithelial cells of the spiral prominence (SP, black broken lines mark the apical surface of SP epithelial cells). In these basal half-turns, OSCs are covered by CCs and the SP epithelial cells and therefore have no direct contact with endolymph. In contrast, in half-turns VI–VIII, OSCs are interposed between CCs and SP epithelial cells and thus are a direct constituent of the PEB. b Confocal images of immunofluorescence labelling of AQP4 (red) and AQP5 (green) in the outer sulcus region of the adult guinea pig cochlea. In half-turns I–VI, AQP4 labelling was detected in the basal membranes of CCs (white arrows). No immunoreactivity for AQP4 and AQP5 was detected in the OSCs of these half-turns. In half-turn VII, AQP4 labelling was observed in the basal membranes of CCs (white arrow), and OSCs showed AQP4 labelling in their basolateral membranes that enwrap their root processes (*, white arrowheads) but were devoid of AQP5 labelling. In the most apical half-turn (VIII), OSCs exhibited AQP4 labelling in their basolateral membranes (inlay *, white arrowheads) and AQP5 labelling in their apical membranes (inlay *, hollow arrowheads). The radial length of the apical membranes of OSCs in half-turn VIII that exhibited immunolabelling for AQP4 and AQP5 was measured as 56.19 ± 2.47 μm (VIII, white dotted line; n = 3). c Representative images of AQP4 (red) and AQP5 (green) immunolabelling on whole-mount preparations of the lateral wall in the half-turns I, IV and VIII that were used for baso-apical length measurements of AQP4 and AQP5 expression in OSCs. In the half-turns I and IV, AQP4 labelling was detected in CCs (white arrows). In the half-turn VIII, OSCs exhibited a polarised labelling of AQP4 (white arrowheads) and AQP5 (hollow arrowheads) in the basolateral root processes and at the apical side of the cells, respectively. d Quantification of the baso-apical length of AQP4 and AQP5 labelling in the outer sulcus region on whole-mount preparations of the cochlear lateral wall from each of the eight half-turns (I–VIII). AQP4 labelling in CCs was observed throughout the entire length of the whole-mount preparations. In OSCs, AQP4 labelling was restricted to a baso-apical length of 928.64 ± 34.68 μm (n = 3) in half-turn VII and 827.04 ± 10.95 μm (n = 3) in half-turn VIII. Additionally, in half-turn VIII, AQP5 labelling was detected in OSCs that also exhibited AQP4 labelling in their root processes along a baso-apical length of 749.86 ± 173.76 μm (n = 3). (dagger, the length of the entire cochlear lateral wall was derived from [32]; double dagger, the baso-apical length of AQP4 labelling in CCs was set equal to the total length of the lateral wall because we did not observe a baso-apical gradient of AQP4 labelling in CCs). Scale bars: (a, b) 20 μm, (c) 10 μm