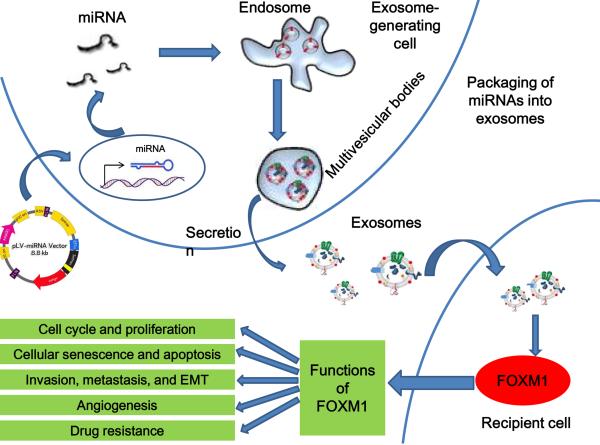
Fig. (2).
Schematic of miRNA transfer by exosomes. MiRNA overexpression is induced via transfection with an miRNA expression vector. MiRNAs are then selectively incorporated into the intraluminal vesicles of multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Exosomes containing miRNAs are derived from the MVBs and may be released into the extracellular environment via either fusion of MVBs with the cell surface or a budding pathway. Exosomes also may bind to the plasma membrane of a target cell. Recruited exosomes may either fuse directly with the plasma membrane or be endocytosed and then fuse with the delimiting membrane of an endocytic compartment. Both of these fusion pathways result in the delivery of exosomal miRNA to the cytoplasm of the target cell, where it may associate with and silence corresponding mRNA.