Figure 6.
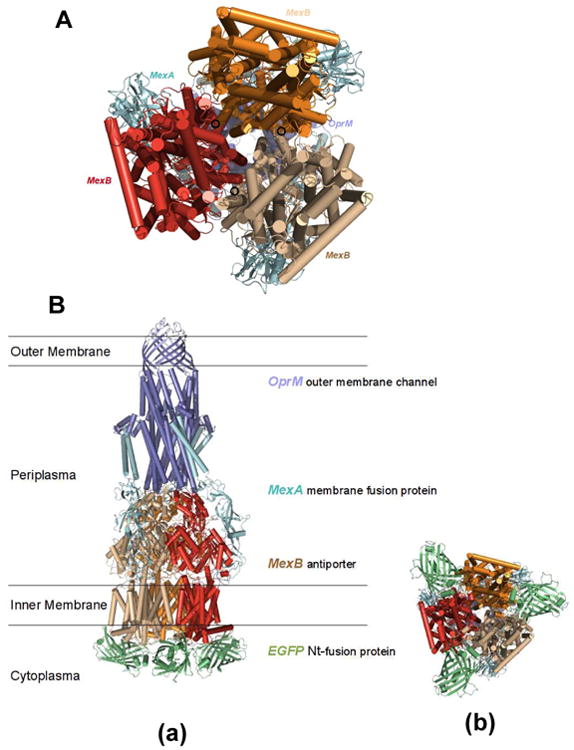
The modeled structures of MexA-(EGFP-MexB)-OprM expressed in the cells (ΔMexB): (A) Secondary structure of MexAB-OprM model is constructed based on the coordinates of the data-driven docking model of the multidrug efflux pump (AcrA-AcrB-TolC) from P. aeruginosa. The model shows the location of the MexB N-termini at the cytosolic end of the translocation pore of the transporter with the unstructured loop of the N-termini pointing inward towards the trimeric pore. (B) The EGFP domains were fused to the N-termini of MexB in its trimer assemblage: (a) stereo side view and (b) bottom view of the structures. Spatial placement of the EGFP domains in the cytosol is limited by potential EGFP to EGFP, or EGFP to MexB clashes in the trimeric configuration. The position and orientation of the N-terminal fused EGFP domains may either partially block the translocation pore or restrict the movement of the individual pump domains, thereby restricting efflux activity.
