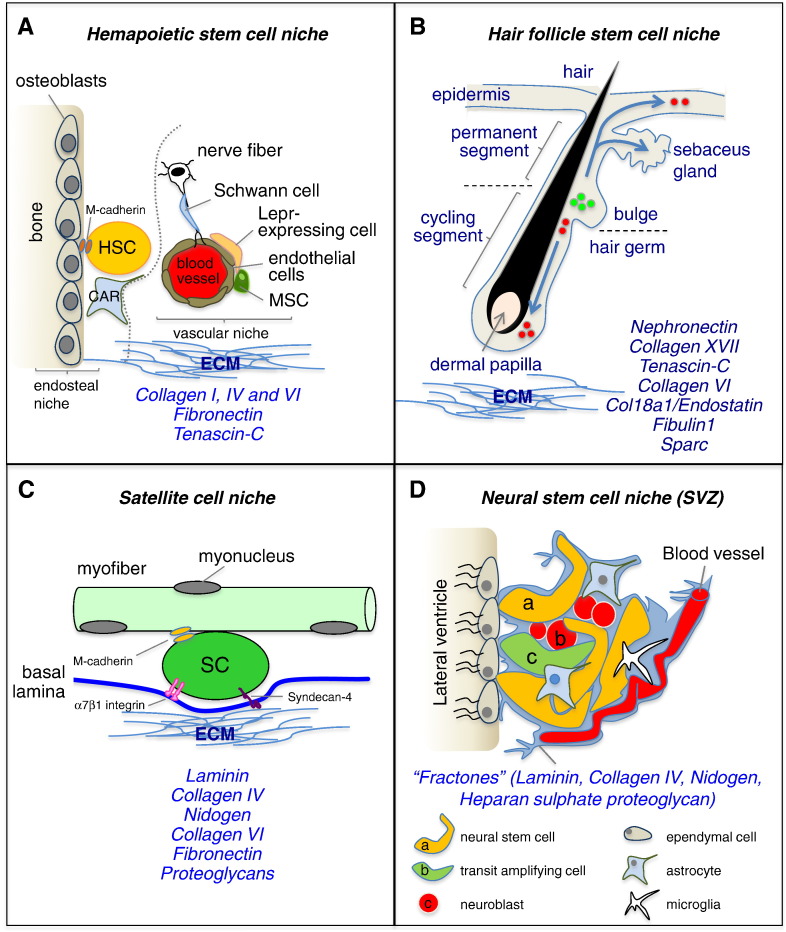
Fig. 5.
Stem cell niches and their ECM. The diagrams show four different stem cell niches, together with their cellular and ECM components. ECM molecules playing major roles in the different niches are indicated. (A) HSC niche consists of two anatomically distinct (dotted line) cellular entities, the “endosteal niche”, populated mainly by osteoblasts, and the “vasculature niche”, located in the perivascular space. HSCs can move through those two niches and interact with ECM molecules. A variety of cells, including osteoblasts, Cxcl12-abundant reticular (CAR) cells, nestin-positive mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), Lepr-expressing perivascular cells, and endothelial cells, were shown to be active components of the niche. (B) Diagram of the hair follicle. Multipotent stem cells are located in the bulge, which lies in the outer root sheath just below the sebaceous gland, and contribute to the lineages of the hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and the epidermis (arrows). The ECM surrounds the dermal papilla, a cluster of specialized mesenchymal cells in the hair bulb. (C) In skeletal muscle, satellite cells reside in the niche between myofiber plasma membrane and basal lamina. The myofiber basal lamina is a network of ECM components, including collagen IV, laminin, collagen VI, fibronectin and proteoglycans, which facilitate satellite cell adhesion via binding to receptors such as α7β1 integrin and syndecan-4. (D) In the adult brain, the SVZ niche is composed of three cell populations that lie immediately beneath a monolayer of ependymal cells lining the lateral ventricle and corresponding to the relatively quiescent NSCs (a), mitotically active transit amplifying cells (b), and neuroblasts (c). NSCs are intercalated into the ependymal layer and are also closely associated with the vasculature. NSCs within the SVZ are in contact with endothelial cells, microglia and astrocytes. NSCs are also in contact with fractones, structures rich in ECM molecules and continuous with the basal lamina of blood vessels.