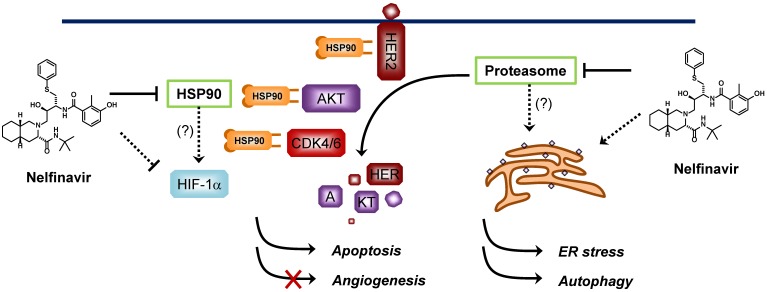
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanisms of anticancer activity of nelfinavir. Nelfinavir is known to have a strong anticancer activity through multiple pathways including induction of ER stress, apoptosis and autophagy, and inhibition of AKT pathway and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α)-dependent angiogenesis. Nelfinavir was shown to inhibit the chymotrypsin- and trypsin-like activities of 20S human proteasome. However, whether anti-proteasome effect is the primary mechanism of nelfinavir for anticancer activity remains elusive since nelfinavir causes proteasome-dependent degradation of several proteins. HSP90 is another proposed molecular target of nelfinavir, of which the inhibition leads to a decrease in the levels of its client proteins including HER2, AKT and CDKs through proteasome-dependent degradation.