Figure 1.
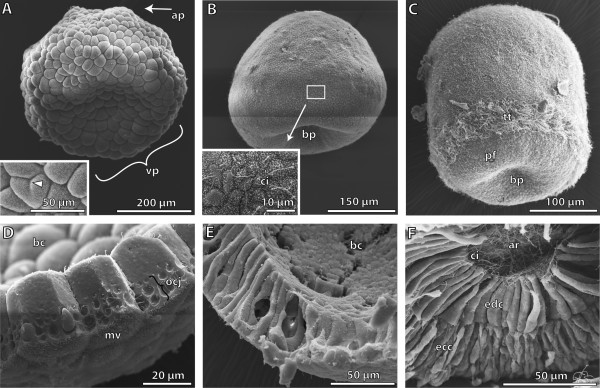
Scanning electron micrographs showing different early embryological stages of Saccoglossus kowalevskii . (A) The 8 hour post fertilization (h pf) blastula shows a prominent depression at the vegetal pole (vp). Inset shows blastomeres at higher magnification (high mag). Partial constrictions demonstrate ongoing cleavage (arrowhead). (B) The flattened gatrula (24 h pf) shows the invagination of the archenteron at the blastoporus region (bp). Inset: a single cilium (ci) is developed on each cell‘s surface. (C) Around 30 h pf gastrulation is completed. Embryos display an elongated shape. The multiciliated telotroch (tt) is developed about 50 μm from the blastopore. (D) The cells of the blastula stage are of cuboid shape, and covered apically with microvilli (mv). The cells are interconnected by occluding cell junctions (ocj). (E) The cells of the gastrula are highly prismatic enclosing the blastocoel (bc). (F) The blastocoel is reduced by the endodermal germ layer almost completely. Endodermal cells (edc) are columnar, bordering the lumen of the archenteron (ar) with their apical cell surface. Long cilia protrude into the lumen. Ectodermal cells (ecc) exhibit a columnar shape, with sometimes very narrow elongated parts, conveying a pseudostratified appearance. ap animal pole, pf perianal field.
