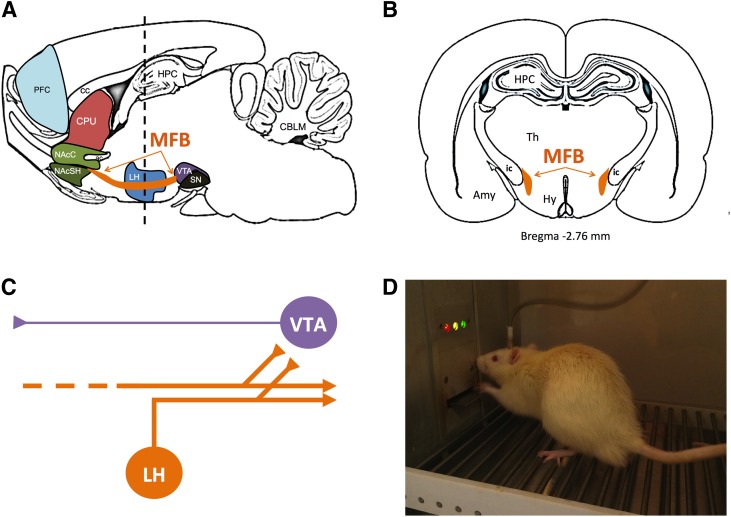
Fig. 1.
Medial forebrain bundle (MFB) as a target for brain stimulation in ICSS studies for abuse potential testing. Sagittal section (A) and coronal section (B) of rat brain showing location of the MFB in orange. (C) Diagram of neurons thought to contribute to ICSS. Electrical stimulation of MFB in ICSS is thought to produce direct activation of “first stage” descending myelinated neurons (orange) that originate in lateral hypothalamus or more rostral regions and project caudally to midbrain and brainstem. Collateral branches of these “first stage” neurons project to and activate “second stage” unmyelinated mesolimbic dopamine neurons (purple) in ventral tegmental area. (D) Photograph of a rat with an MFB electrode in an operant chamber. Amy, amygdala; CBLM, cerebellum; cc, corpus callosum; CPU, caudate/putamen; ic, internal capsule; HPC, hippocampus; Hy, hypothalamus; LH, lateral hypothalamus; NAcC, nucleus accumbens core; NAcSH, nucleus accumbens shell; PFC, prefrontal cortex; SN, substantia nigra; Th, thalamus; VTA, ventral tegmental area.