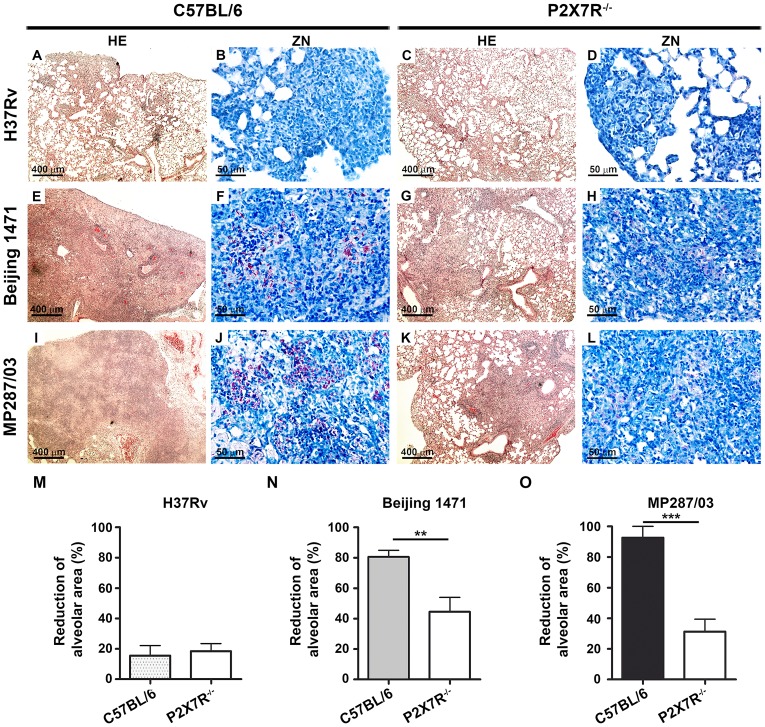
Figure 3. Lung histopathology in C57BL/6 and P2X7R−/− mice on day 28 p.i. with hypervirulent mycobacteria.
C57BL/6 and P2X7R−/− mice were infected i.t. with approx. 100 bacilli of H37Rv Mtb, Beijing 1471 Mtb and MP287/03 Mbv. (A–L) Images show representative lung sections stained with HE (50× magnification; bar scales correspond to 400 µm) and ZN (400× magnification; bar scales correspond to 50 µm) methods. (A and C) H37Rv Mtb-infected C57BL/6 and P2X7R−/− mice exhibited incipient granulomas. (B and D) Amplification of the inflamed areas shows no visible BAAR in the mice presented in B and D. (E and I) Beijing 1471 Mtb- and MP287/03 Mbv-infected C57BL/6 mice displayed extensive lung TB lesions with areas of necrosis. (F and J) Numerous BAARs were observed in the lesions described in E and I. (G and K) Beijing 1471 Mtb- and MP287/03 Mbv-infected P2X7R−/− mice presented with small lung lesions with no visible necrosis. (H and L) Reduced amounts of BAARs were observed in the lesions described in G and K. (M) Morphometric quantification of lung sections shows a reduction in the intralveolar areas in infected mice compared to non-infected controls (means ± SD, n = 3–5). Significant differences were observed for the indicated groups (**p<0.01 and ***p<0.001). The data are representative of three separate experiments.