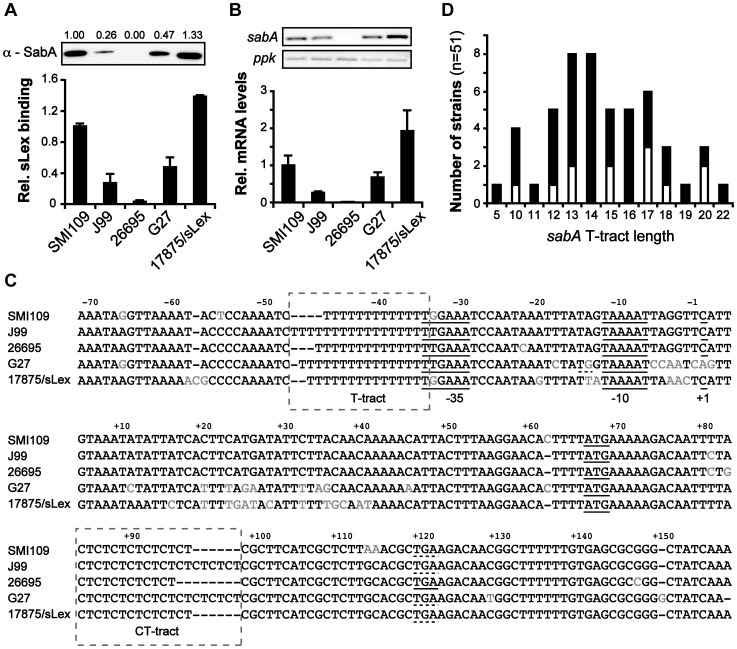
Figure 1. Interstrain variation of sabA mRNA levels, SabA protein expression and functional sLex-receptor binding.
A) Analysis of SabA expression and sLex-receptor binding activity in a set of five H. pylori strains. Image shows one representative immunoblot analysis with α-SabA antibodies and the numbers above represents SabA expression quantification, with expression in strain SMI109 set to 1. Equal amounts of crude protein extracts were loaded in each lane (Fig. S10A). The graph shows binding to soluble 125I-sLex-receptor conjugate of the same strains as analyzed in the immunoblot. Bacteria were grown on plate as described in Materials and Methods prior to the analysis. Average and standard deviations are calculated from at least two independent experiments and duplicate samples/analysis of each strain. B) RT-qPCR analysis of sabA mRNA levels in the same set of strains as in Fig. 1A. The sabA mRNA levels were normalized to a set of reference genes and data is presented as relative, with the levels in strain SMI109 set to 1. Images show one representative semi-quantitative PCR analysis, using the same primers as in the RT-qPCR analysis; sabA-2 and ppk-2. C) Sequence comparison of the PsabA region (−71 to +158, relative to the transcriptional start site) between different H. pylori strains. The +1 transcriptional start sites, as determined by primer extension and 5′-RACE, and the predicted −10 and −35 promoter elements, are underlined. Differences in nucleotide sequences are shown in grey color. The regions containing the T-tract and CT-repeats are boxed. The stop codon (TGA) that results in a truncated SabA protein in the CT6-off strain 26695 is also underlined. A more extensive comparison, of 44 PsabA sequences, is shown in Fig. S2. D) Distribution of T-tract lengths in the sabA promoter (PsabA) of 51 sequenced H. pylori strains. Black represents number of analyzed genome-sequenced strains, whereas white represents the number of strains where the sequence of the sabA locus was obtained after conventional PCR amplification.