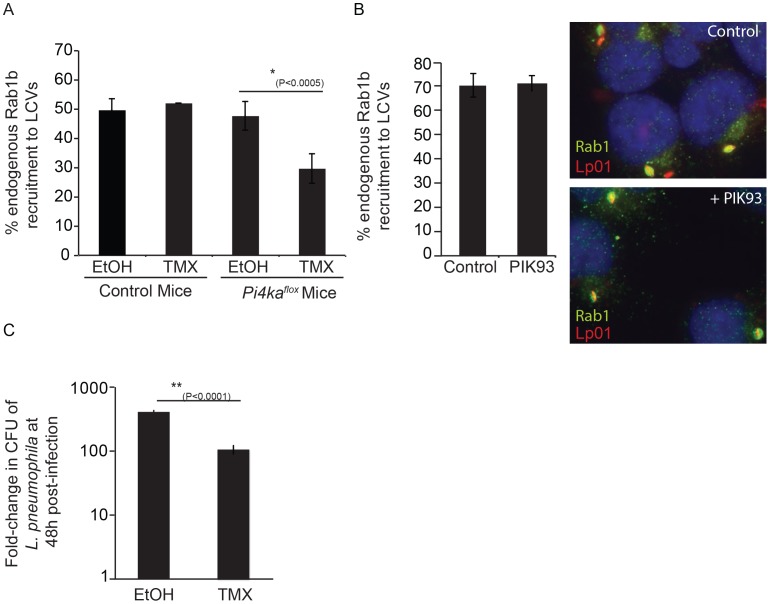
Figure 9. Influence of PI4KIIIα knockout on DrrA-mediated recruitment of Rab1b to LCVs in bone-marrow derived macrophages (BMM).
(A) After treatment of BMM obtained from C57BL/6 or conditional PI4KAflox mice with either ethanol (EtOH) or (Z)-4-hydroxytamoxifen (TMX), which induces cre-mediated deletion of floxed PI4KIIIα, BMM were infected with wild type L. pneumophila expressing GFP for 1 h before fixation. Graph shows quantification of endogenous Rab1b recruitment to LCVs from three independent experiments with at least 150 vacuoles counted per treatment (EtOH/TMX) and mouse donor (C57BL/6/PI4KAflox) for each experiment. (B) Quantification of endogenous Rab1b recruitment to LCVs formed by Lp01+pAM239 in HEK293 FcγRII at 1 hour post-infection in cells treated with either DMSO (control) or 2 µM PIK93. Drugs were added to wells 30 min prior to infection and maintained throughout the subsequent steps. Data shown was obtained from 3 independent experiments with >200 vacuoles assessed for Rab1 recruitment for each condition per experiment. (C) Graph showing fold-difference in colony forming units (CFU) of L. pneumophila JR32ΔflaA at 48 hours post-infection compared to time zero. Results are from 18 wells from 2 inoculums per treatment (EtOH/TMX) and mouse donor (C57BL/6/PI4KAflox) for each time point from one experiment. No statistical differences were observed between the separate inoculums for each cell-type/treatment and results were averaged to give the final values. Error bars represent the SEM for fold-differences obtained for each condition. A decrease in L. pneumophila replication in TMX-treated PI4KAflox BMDM was also observed in two additional independent experiments.