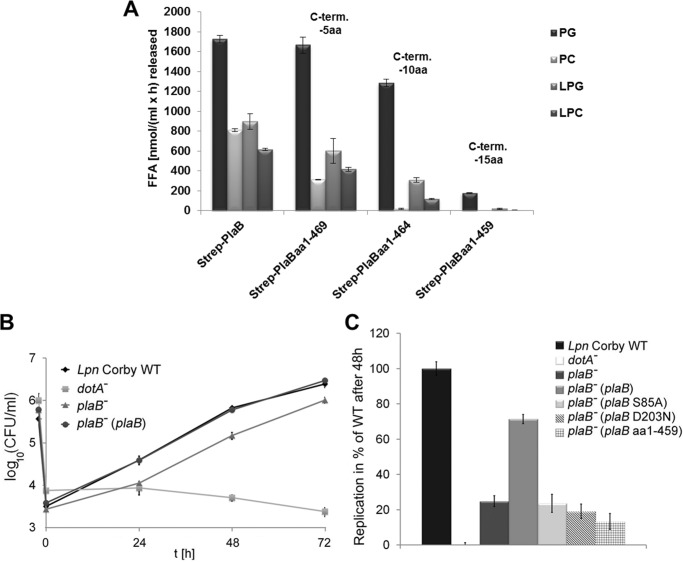
FIGURE 5.
Entire C-terminal 15-amino acid region of PlaB is essential for lipolytic activity, and PlaB lipolytic activity is required for optimal intracellular replication. A, purified rStrep-PlaB and truncated variants were analyzed for enzymatic activities. Release of free fatty acid (FFA) was detected after incubation of 0.04 μg/ml (0.72 nm) purified rStep-PlaB and truncated variants with phospholipids for 45 min. C-term aa, C-terminal amino acid. RAW 264.7 macrophages were infected with L. pneumophila wild type, dotA−, and plaB− mutants and the complementing strain plaB−(plaB) expressing intact PlaB (B). C, RAW 264.7 macrophages were also infected with the plaB− mutant expressing active PlaB from pJB04, catalytic mutants expressing inactive PlaB from pJB06 and pJB12, or C-terminal truncated inactive PlaB from pKK50 at multiplicities of infection of 1. The dotA− strain was used as a virulence-attenuated control. The time point −2 h denotes the bacterial inoculum when the 2-h uptake period was started. At various time points before and after the uptake period, bacteria were quantified by plating aliquots on BCYE agar. The result represents the means ± S.D. of triplicate samples and are representative of at least two additional experiments. Replication of plaB− strains expressing plaB S85A, plaB D203N, or plaB aa1–459 and dotA− was significantly different from the wild type (*, p < 0.005, Student's t test, n = 3). PG, dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol; PC, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine; LPG, 1-monopalmitoyl-lysophosphatidylglycerol; LPC, 1-monopalmitoyllysophosphatidylcholine.