FIGURE 4.
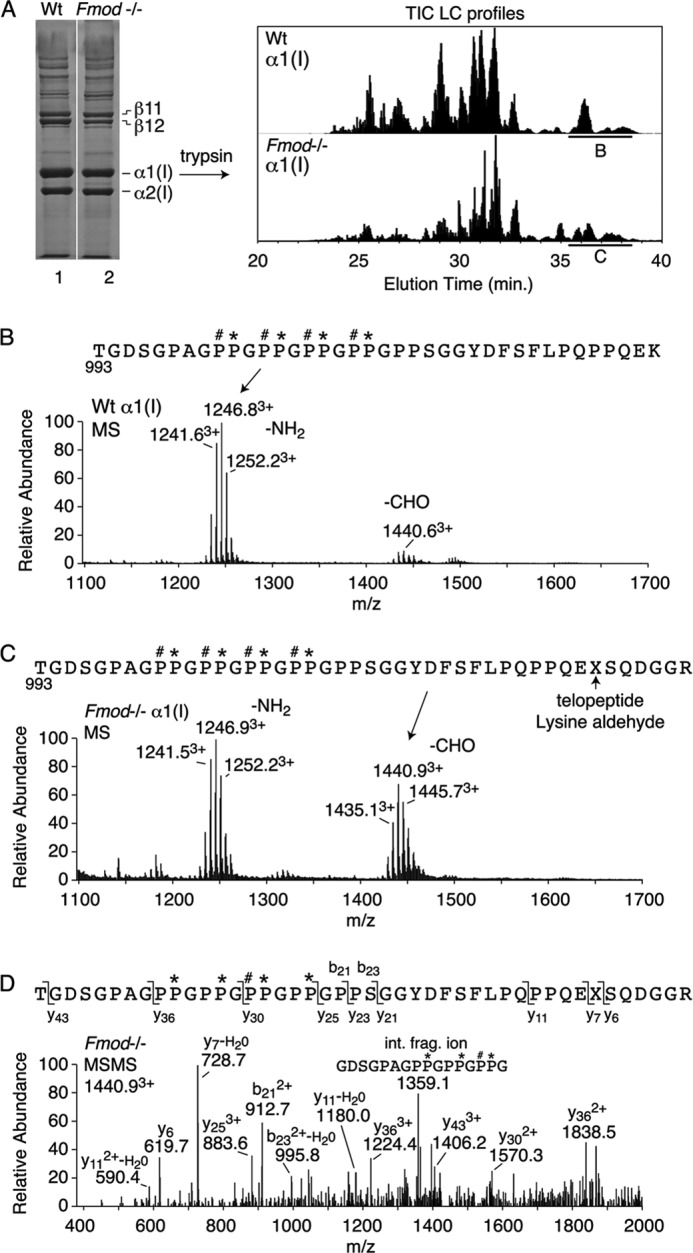
Mass spectral analysis of the C-terminal domain of collagen α1(I) chains extracted from Fmod−/− and wild-type tendons. A, heat-denatured extract of tendon collagen was run on 6% SDS-PAGE, and excised α1(I) chains were digested in-gel with trypsin and the peptides profiled by LC-tandem mass spectrometry. B–D, the C-terminal tryptic peptide domain (underlined in total ion current (TIC) profile), identified by MSMS fragmentation (D), showed more of the longer aldehyde-containing peptide from Fmod−/− tissue (C) than from wild type (B). Note that the (GPP)5 C terminus of the triple-helix is equally modified with up to four 3-hydroxyproline residues per chain in both Fmod−/− and wild-type tendon collagen, a post-translational modification that is peculiar to tendon (4).
