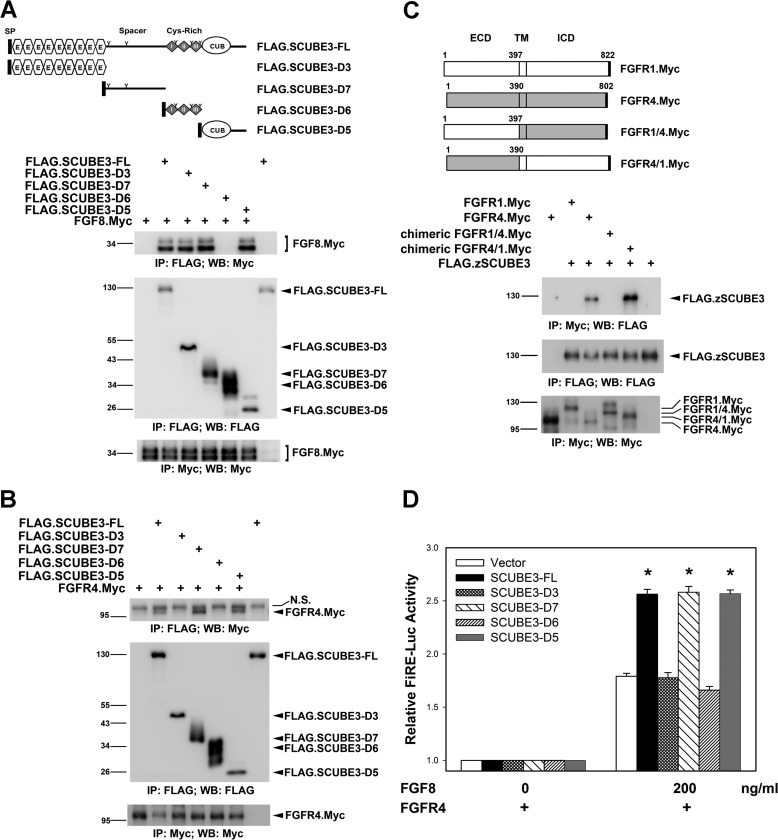
FIGURE 4.
Molecular mapping for the functional domain of SCUBE3. A and B, the spacer and CUB domain of SCUBE3 can interact with FGF8 and FGFR4. The expression plasmid encoding Myc-tagged FGF8 (A) and Myc-tagged FGFR4 (B) was transfected alone or together with a series of FLAG-tagged SCUBE3 deletion constructs in HEK-293T cells as depicted on top of A. After 2 days, cell lysates were prepared and underwent immunoprecipitation, followed by Western blot analysis with indicated antibodies to determine the protein-protein interactions. IP, immunoprecipitation; N.S., nonspecific band; WB, Western blot. C, FGFR4 interacts with SCUBE3 through its extracellular domain. Myc-tagged FGFR1, FGFR4, and chimeric FGFR1/4 or FGFR4/1 expression plasmids were transfected alone or with the FLAG-tagged SCUBE3 in HEK-293T cells. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments were performed as described above to examine the protein-protein interactions. ECD, extracellular domain; TM, transmembrane domain; ICD, intracellular domain. D, SCUBE3 augments FGF signaling through its spacer region or CUB domain. HEK-293T cells were transfected with FiRE-Luc and pRL-TK alone (blank bars) or with the expression plasmid encoding FL or various SCUBE3 domain deletion constructs combined with FGFR4 expression plasmid. Transfected cells were incubated with or without FGF8 (200 ng/ml) for 24 h, and then luciferase activity was measured. Firefly luciferase values were normalized to Renilla activity to obtain relative luciferase activity. The data are means ± S.E. *, p < 0.05.