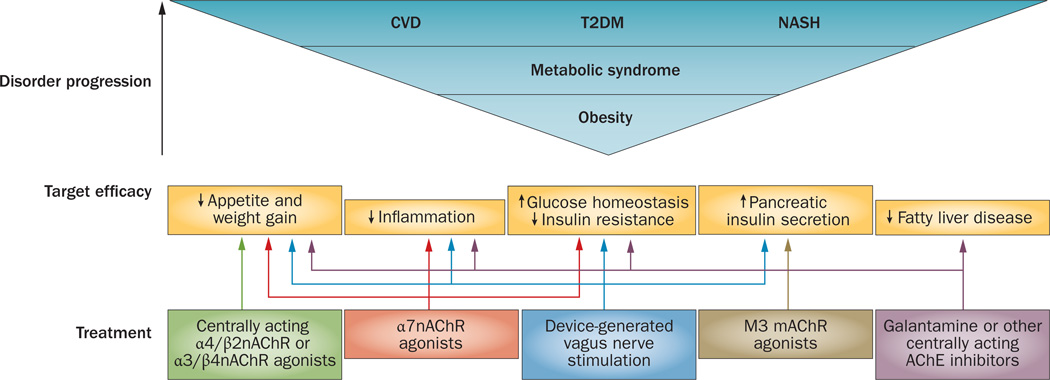
Figure 4.
Possible therapies based on cholinergic-based approaches for the treatment of obesity-driven disorders. Obesity progression and the metabolic syndrome are closely associated with debilitating diseases, including T2DM, CVD and NASH. Dysregulated immune and metabolic homeostasis is associated with inflammation underlying obesity-related disease pathogenesis, which mediates insulin resistance and other complications. Efficacy of cholinergic agents in activating regulatory mechanisms in the inflammatory reflex in animals indicates a rationale for developing novel treatments for humans. Cholinergic therapeutics and devices for vagus nerve stimulation could selectively control the complex interplay between immune and metabolic pathways. Abbreviations: CVD, cardiovascular disease; M3 mAChR, M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor; α7nAChR, α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; α4/β2nAChR, α4/β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; α3/β4nAChR, α3/β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; VNS, vagus nerve stimulation.