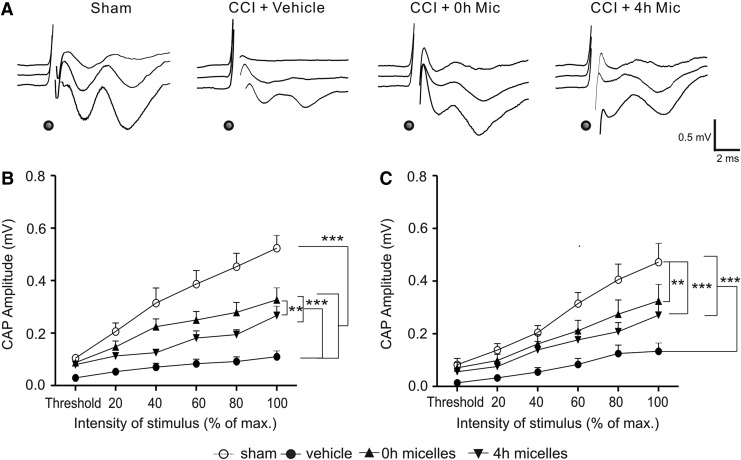
FIG. 2.
Intravenous injection of the micelles within 4 h after controlled cortical impact (CCI) improved the function of myelinated and unmyelinated axons of the corpus callosum. (A) Representative traces of compound action potentials (CAPs) evoked at threshold (top traces), 2× threshold (middle traces), and maximum (bottom traces) stimulation intensities in the sham, CCI+vehicle, CCI+0h micelles, and CCI+4h micelles groups. The times of stimulation are marked with black dots. (B,C) Input-output curves of mean N1 (B) and N2 (C) peak amplitudes evoked at increasing stimulation intensities in the four groups. CCI resulted in significant decreases in both N1 and N2 amplitudes. Injection of the micelles at 0 h or 4 h after injury improved the recovery of N1 and N2 amplitudes. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Group sizes (mice): Sham=14; CCI+vehicle=11; CCI+0 h micelles=13; CCI+4 h micelles=12.