Figure 1.
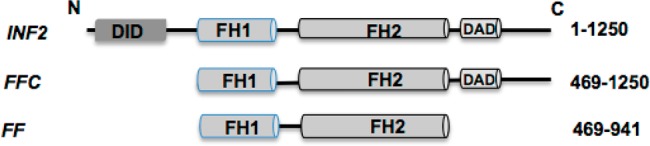
Schematic representation of the domain organization of inverted formin 2 (INF2) showing regions important for actin binding and protein–protein interactions. Formin constructs used in this study include INF2-FH1-FH2-C, also termed INF2-FFC, and INF2-FH1-FH2 (INF2-FF). N and C denote the N- and C-termini, respectively, of protein sequences. Other abbreviations are DID (diaphanous inhibitory domain), FH1 (formin homology 1), FH2 (formin homology 2), and DAD (diaphanous autoregulatory domain).
